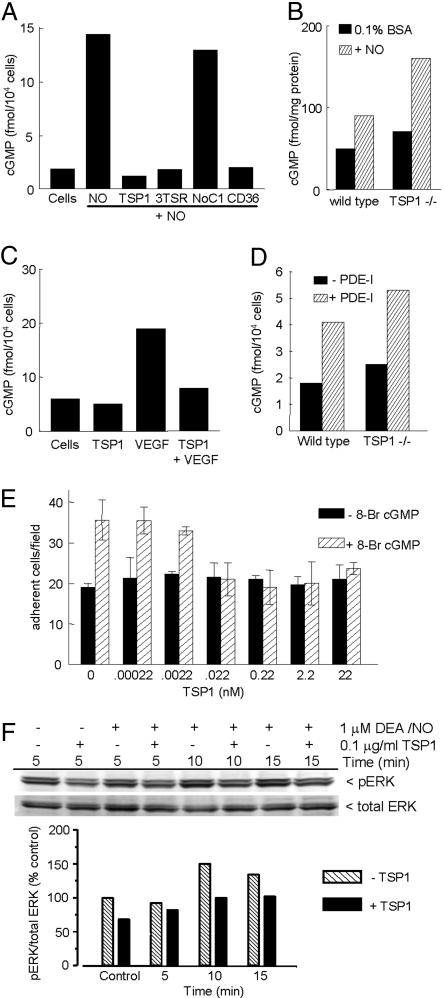
Fig. 5.
TSP1 inhibits NO-induced cGMP synthesis and signaling downstream of cGMP in endothelial cells. (A) HUVECs (5 × 103 per well) were weaned from EGM plus 5% FCS to 0.1% BSA as described in Supporting Text and treated with 10 μM DEA/NO for 5 min in the absence or presence of 100 pM of TSP1, 3TSR, NoC1, or CD36 antibody. Mean intracellular cGMP levels from duplicate determinations are presented for a representative experiment. (B) Intracellular cGMP was determined for weaned unstimulated TSP1 null and WT lung endothelial cells and cells treated for 5 min with 10 μM DEA/NO. (C) Intracellular cGMP was analyzed in weaned HUVECs after treatment with 1 μg/ml TSP1 with or without VEGF (30 ng/ml) for 10 min. (D) WT and TSP1 null lung-derived endothelial cells (5,000 cells per well) were incubated for 30 min in EGM plus 0.1% BSA with or without inhibitors of cGMP PDEs [PDE1 (25 μM 8-methoxymethyl-3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine], PDE2 (20 nM erythro-9-[3-(2-hydroxynonyl)]adenine·HCl), and PDE5 [1 μM 4-{[3′,4′-(methylenedioxy)-benzyl}amoni)-6-methoxyquinazoline)], and intracellular cGMP levels were determined. (E) Modulation of endothelial cell adhesion to 5 μg/ml type I collagen was tested with 10 μM 8Br-cGMP stimulation with or without TSP1. Results are from three separate experiments. (F) HUVECs were harvested 0, 5, and 15 min after addition of 1 μM DEA/NO in medium containing 5% serum, brain extract, and heparin. Cell lysates were resolved on SDS gels and blotted with anti-ERK and phospho-ERK (pERK).