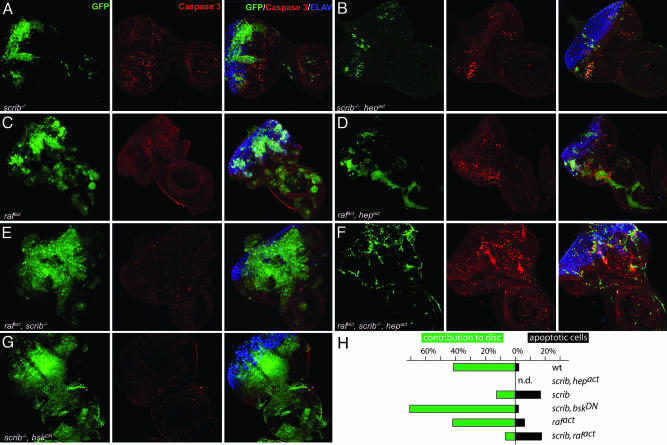
Fig. 3.
Activation of JNK-signaling pathway induces apoptosis in scrib–/– and rafact clones as well as in scrib–/–, rafact clones. Eye-antennal discs were dissected from third instar larvae and analyzed by immunostaining and confocal microscopy. All images were taken at the same magnification (×40) and represent projections of multiple sections. Mutant clones of the indicated genotypes are marked by GFP fluorescence (Left, green). Introduction of an activated allele of JNKK (hepact)(B, D, and F) significantly suppressed the expansion of benign scrib–/– (A) and hyperproliferative rafact (C), or malignant scrib–/–, rafact (F) clones. Many cells within the clones underwent apoptosis as shown by staining with anti-active caspase 3 antibody (Center, red). Moderately elevated levels of apoptosis, which are not restricted to the GFP-marked mutant areas, are consistently observed in eye-antennal discs containing scrib–/– clones (A). Developing photoreceptors are shown by Elav staining (Right, blue). Neuronal differentiation is severely impaired in scrib-null clones in all genotypes. Note that micrographs are not representative of the size of the different imaginal disc because the preparation for confocal microscopy may distort the dimensions of the organ.