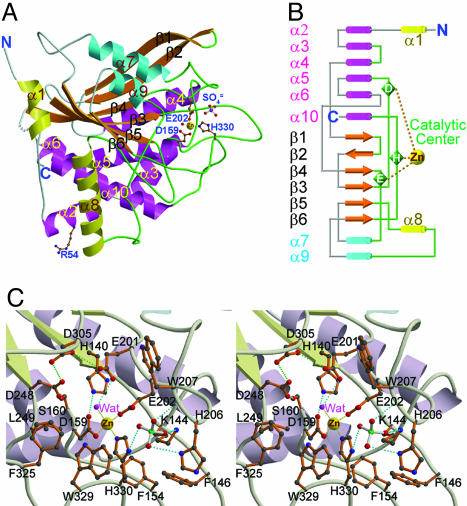
Fig. 1.
Structure of human QC. (A) A ribbon diagram of the overall structure of human QC. The central six β-strands are colored orange. The α-helices located on the top, bottom, and edge are colored cyan, magenta, and yellow, respectively. The zinc ion is shown as a yellow sphere. The zinc-coordinated residues, Arg-54 (genetic mutation to Trp residue occurred frequently in adult women with osteoporosis), and a sulfate ion are depicted with a ball-and-stick model. The coils and loops adjacent to the catalytic center are painted green, whereas those distant from the active site are colored gray. Gray dots represent the disordered region of residues 183–188. (B) A topology diagram of the human QC structure. The color codes for secondary structural elements are identical to those in A.(C) A stereoview of the human QC catalytic region. The active-site residues in conf-A are shown and labeled. Possible hydrogen and coordination bonds are represented with dotted lines colored cyan and yellow, respectively. The green dotted lines depict the possibly unusual hydrogen bonds between D305 and E201 (3.06 Å) and between D305 and D248 (2.53 Å).