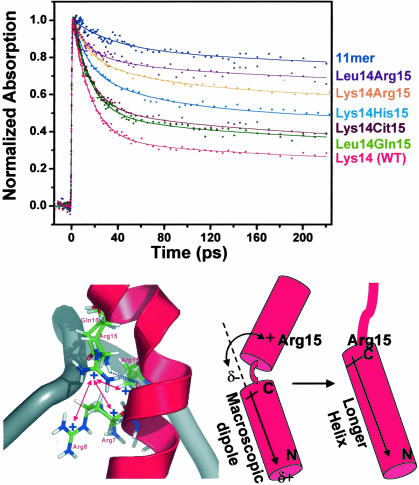
Fig. 4.
Structural effects on dynamics. (Upper) Effects of amino acid residues at position 15 of N peptides on the amplitude of ultrafast component in the transient absorption experiments with position 14 being either Lys or Leu. The decay profile for 11-mer complex is included as a no-ultrafast component control. (Lower Left) Structural model for the Arg cluster interacting with Arg-15 in the complex. Only part of the backbone of RNA is shown; the bases are removed for clarity. Blue dotted lines represent the H-bonds from either Gln-15 in the WT and Arg-15 mutants (modeled based on ref. 37) to the main-chain carbonyl of Arg-8. The positively charged Arg cluster formed by Arg-7, -8, and -11 is labeled. Red double arrows indicate potential repulsive interactions between Arg-15 and the Arg cluster. (Lower Right) Interaction between Arg-15 and the macroscopic dipole moment (indicated by the arrow) in the stacked and helix-extended complexes. The positive charge favors a longer, straighter helix that terminates at Arg-15 (see text).