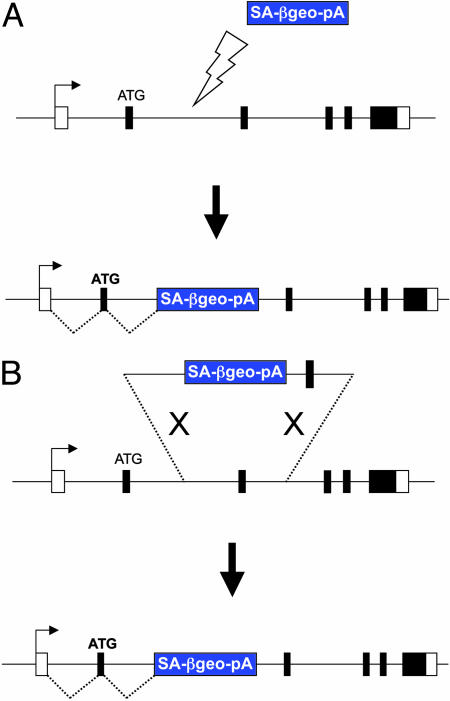
Fig. 1.
Gene trapping versus targeted trapping. (A) Gene trapping depends on random insertions of a promoterless reporter gene, such as βgeo, equipped with splice acceptor (SA) and polyadenylation (pA) signals. The reporter is activated after insertions into introns of expressed genes to generate a fusion mRNA that can be characterized by 5′ RACE. (B) Targeted trapping relies on homologous recombination to introduce a promoterless gene-trap cassette into predefined loci. The trapping cassette is flanked by genomic sequences of the target locus that do not contain the promoter of the target gene.