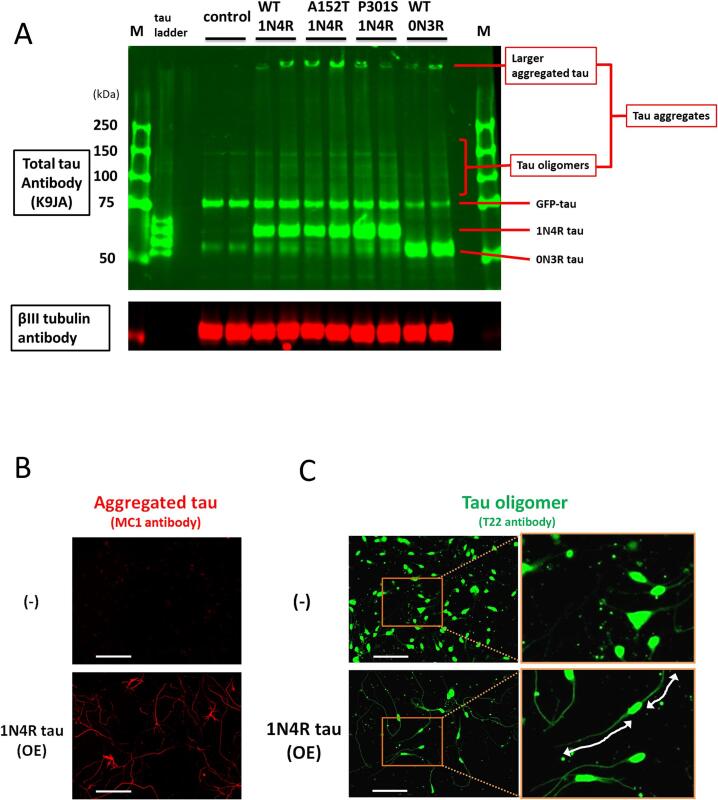
Fig. 2.
Tau overexpression induces tau aggregation in iPSC-derived neurons. (A) In addition to monomeric tau species, larger aggregated tau at the top of the gel and tau oligomers in the middle of the gel after overexpression of WT (1N4R), A152T (1N4R), P301S (1N4R) and WT (0N3R) tau using lentivirus particles were detected by Western blot of non-reducing SDS-PAGE using total tau antibody. Lentivirus particles were infected at MOI 3, and the cells were harvested on day 5 after tau overexpression. βIII tubulin antibody was used as a loading control. control: lentivirus without tau expression treatment group. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of aggregated tau (oligomers and filaments) in hiPSC-derived neurons after tau overexpression using MC1 antibody (red). (−): lentivirus-untreated group. Neurons were treated with 1N4R tau lentivirus (MOI 10) and fixed on day 7 after tau overexpression. Scale bars, 100 µm. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of tau oligomers in hiPSC-derived neurons after tau overexpression using T22 antibody (green). (−): lentivirus-untreated group. Neurons were treated with 1N4R tau lentivirus (MOI 10) and fixed on day 5 after tau overexpression. Even without exogenous tau introduction, we detected T22 signals in the cell somas. Representative tau overexpression-dependent signals are indicated by white bars and arrows. Scale bars, 100 µm.