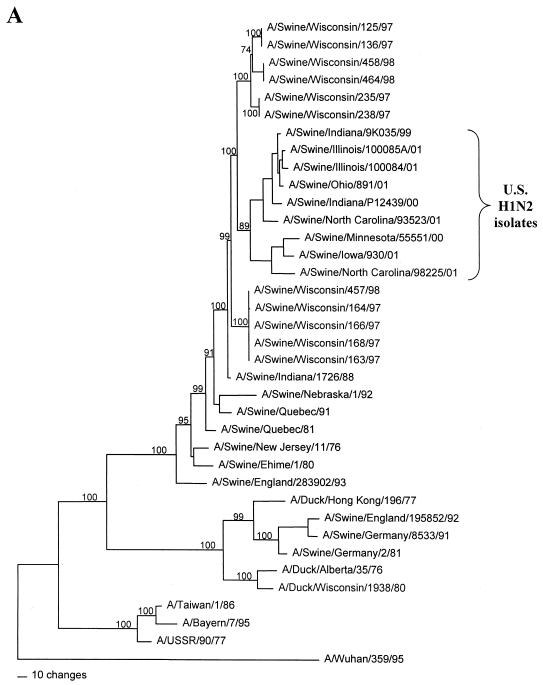
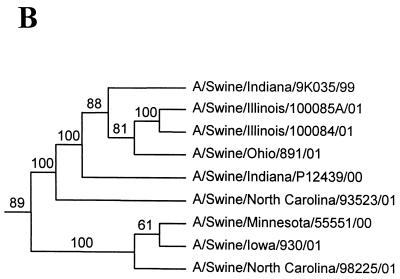
FIG. 1.
Nucleotide phylograms for the HA genes of swine H1N2 and reference influenza viruses. The evolutionary relationships among these viruses were estimated by the method of maximum parsimony (PAUP software, v.4.0b6; David Swofford, Smithsonian Institution) by using a heuristic search algorithm with the MULTREES option in effect. The numbers at the nodes of the phylograms represent confidence levels for the phylogram topologies as determined by bootstrap analysis with 500 replications. (A) Overall phylogram. Horizontal-line distances are proportional to the minimum numbers of nucleotide changes needed to join nodes and gene sequences. The vertical lines are present simply for spacing the branches and labels. The complete phylogram shown represents the best (score = 1,523) of 64,280 rearrangements generated. (B) Detailed depiction of only the H1N2 viruses isolated recently from pigs in the United States in order to demonstrate the bootstrap values within this cluster of viruses.