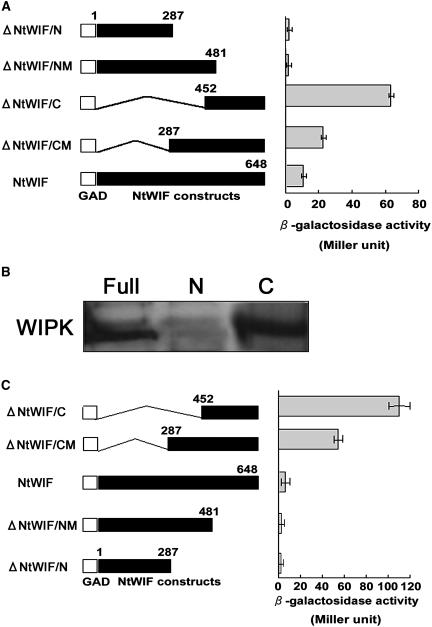
Figure 2.
Interaction between NtWIF and WIPK. A, Yeast two-hybrid assay. Yeast Y190 cells were cotransformed with GBD-WIPK and various combinations of GAD-NtWIF constructs as indicated on the left. Transformants from the SD/-HTL agar plate were cultured in SD/-TL broth for β-galactosidase enzymatic assays using o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside as substrate (triplicate experiments). B, Pull-down assay of recombinant WIPK and NtWIF. Interaction was tested using GST-fused full-length NtWIF (Full), ΔNtWIF/C (C) and ΔNtWIF/N (N) proteins expressed in Sf9 cells and bacterially expressed His-tagged WIPK protein. NtWIF-GST proteins were bound to a glutathione column, and His-tagged WIPK was added. After elution with reduced glutathione, proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, and WIPK was detected by anti-His-tag antibodies. C, Intramolecular interaction between the B3 domain and the WIPK-interacting domain. Yeast Y190 was transformed with the indicated GAD-NtWIF constructs and a GBD-ΔNtWIF/N. Yeast transformants were plated on SD/-HTL/+3-amino-1,2,4-triazole agar, and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactopyranoside filter and β-galactosidase assays were performed as described above. The number beside each column represents the number of amino acids encoded by the respective peptide.