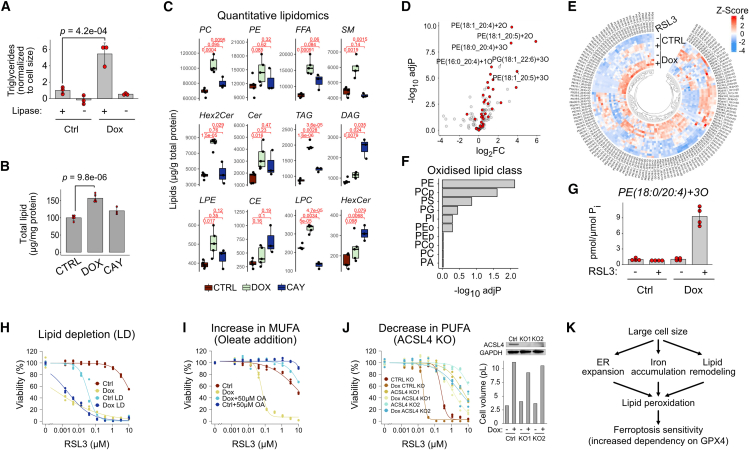
Figure 5.
Lipid accumulation and remodeling in large cells
(A) Triglyceride levels normalized to cell size in control and doxorubicin-treated cells. No lipase controls show assay background originating from free glycerol. Data shown are mean ± SD, n = 3.
(B) Total lipids in control, doxorubicin, and desaturase inhibitor CAY10566 (CAY) by quantitative lipidomic analysis by mass spectrometry. Total lipid signals were integrated and normalized to protein concentration. Data shown are mean ± SD, n = 5, except for CAY for which only three replicates were used.
(C) Quantification of different lipid classes. Statistical significance by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test.
(D) Volcano plot showing log2 fold changes and significance of the changes in oxidized lipids between doxorubicin-treated and control cells after RSL3 addition. Phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) are in red.
(E) Heatmap of the redox lipidomic data (see Data S6 for details).
(F) Enrichment of oxidized lipids in different lipid classes. The subscripts o and p refer to oxidized and phosphorylated lipid, respectively.
(G) Quantification of a ferroptotic lipid marker PE(18:0/20:4)+3O. Data shown are mean ± SD, n = 4.
(H) Ferroptosis sensitivity of control and doxorubicin-treated RPE1 cells in the presence of normal or lipid depleted serum (LD).
(I) Ferroptosis sensitivity of control and doxorubicin-treated RPE1 cells with exogenous addition of 50 μM oleate (OA).
(J) Sensitivity of control KO cells and two clones of ACSL4 KO cells (KO1 and KO2) to RSL3 with and without doxorubicin treatment. Inset shows western blot with ACSL4 antibody and measured cell sizes.
(K) Model of ferroptosis sensitization involving ER expansion (Figure 3), iron accumulation (Figure 4), and lipidome remodeling (this figure). See also Figure S5, Data S5, and S6. Abbreviations: PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; FFA, free fatty acid; SM, sphingomyelin; Hex2Cer, dihexosylceramides ; Cer, ceramide; TAG, triacylglycerol; DAG, diacylglycerol; LPE, lysophosphatidylethanolamine; CE, cholesteryl ester; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; HexCer, hexosylceramide; PA, phosphatidic acid; PG, phosphatidylgylcerol; PGP, phosphatidylgylcerolphosphate; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PS, phosphatidylserine.