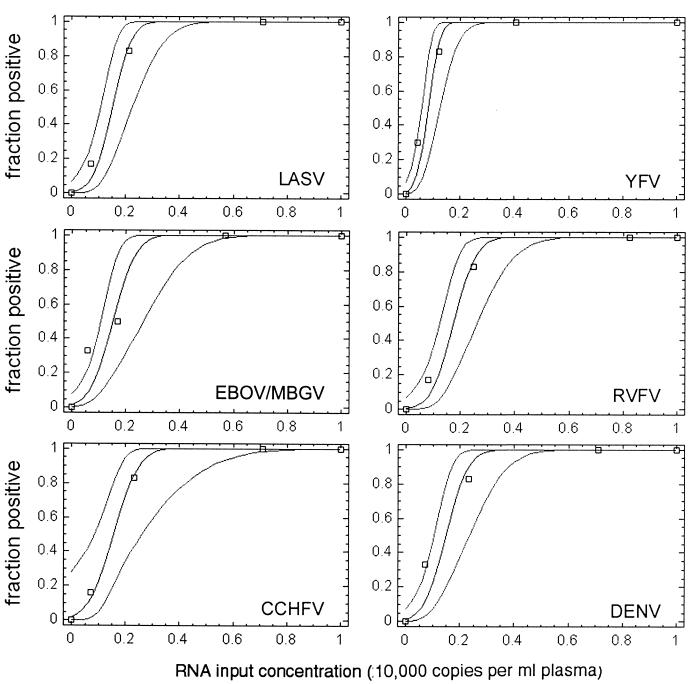
FIG. 3.
Determination of RT-PCR detection limits by probit regression analysis. Negative human plasma was spiked with defined amounts of in vitro-transcribed RNA and prepared three times in parallel. Each RNA preparation was amplified two times in parallel, resulting in six replicate RT-PCRs per RNA test concentration. The experimentally determined fraction of positive reactions (npositive/ntested) (y axis) at the corresponding RNA test concentration (copies per milliliter of plasma) (x axis) is shown by squares. The calculated regression curves (middle curve) indicate the probability (y axis) of obtaining a positive result at any RNA concentration. The 95% confidence intervals for this probability are shown by curves at the left and right of the middle curve. The RNA concentration at which a positive result is achieved with a probability of 95% is given in the text.