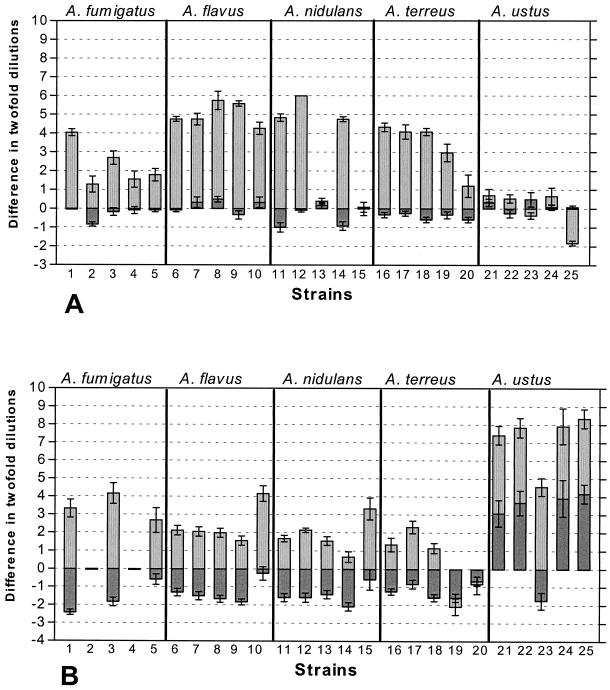
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the results of testing of the susceptibilities of 25 Aspergillus strains to amphotericin B (A) and itraconazole (B) on the basis of the results of the Sensititre and the Etest methods compared with those of the NCCLS method after 48 h of incubation. The MIC endpoints defined in footnotes a and b of Table 3 were used. The MICs obtained by the NCCLS method are represented by the line with 0 difference in twofold dilutions. Bars represent differences in twofold dilutions between the MICs obtained by the NCCLS method and those obtained by the Sensititre method (bars with heavy shading) and the Etest method (bars with light shading) by four different observers in triplicate for each strain of the five Aspergillus species tested (indicated above each panel). Error bars represent the standard errors of the means for the 12 differences (four observers × three replicates) for each strain. The geometric means of the 12 MICs (four observers × three replicates) obtained by the NCCLS method, represented by the line with 0 difference in twofold dilutions, were as follows for amphotericin B (A): for A. fumigatus strains 1 to 5, 1, 3.56, 1.41, 1.19, and 1.26 mg/liter, respectively; for A. flavus strains 6 to 10, 2.12, 1.41, 1.26, 1.26, and 2.52 mg/liter, respectively; for A. nidulans strains 11 to 15, 2.24, 1, 0.5, 2.38, and 0.59 mg/liter, respectively; for A. terreus strains 16 to 20, 2.52, 2.38, 3, 3.78, and 3.21 mg/liter, respectively; and for A. ustus strains 21 to 25, 2.67, 1.89, 1.5, 1.78, and 1.89 mg/liter, respectively. The geometric means of the 12 MICs (four observers × three replicates) obtained by the NCCLS method, represented by the line with 0 difference in twofold dilutions, were as follows for itraconazole (B): for A. fumigatus strains 1 to 5, 0.4, >32, 0.31, >32, and 0.4 mg/liter, respectively; for A. flavus strains 6 to 10, 0.22, 0.19, 0.21, 0.17, and 0.22 mg/liter, respectively; for A. nidulans strains 11 to 15, 0.18, 0.14, 0.16, 0.14, and 0.17 mg/liter, respectively; for A. terreus strains 16 to 20, 0.12, 0.15, 0.18, 0.19, and 0.13 mg/liter, respectively; and for A. ustus strains 21 to 25, 1.59, 1.78, 0.94, 1.5, and 1.78 mg/liter, respectively.