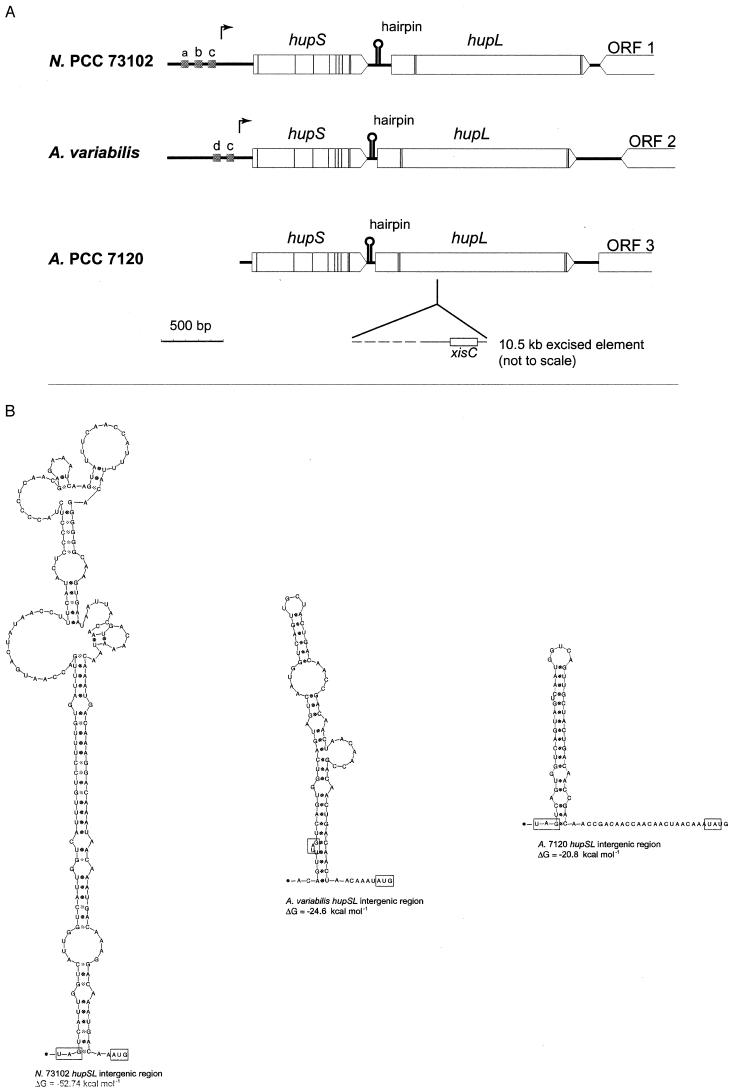
FIG.3.
hupSL in the cyanobacteria Nostoc strain PCC 73102 (N. PCC 73102) (150), A. variabilis ATCC 29413 (79), and Anabaena strain PCC 7120 (A. PCC 7120) (39). (A) Thin vertical lines correspond to the nucleotide triplets encoding the conserved cysteine residues compared to HupSL in other organisms. Arrows show the positions of transcriptional start in Nostoc strain PCC 73102 and A. variabilis ATCC 29413. Grey boxes (a, b, c, and d) indicate the positions of putative promoter elements; a, NtcA-binding site; b, IHF-binding site; c, −10 promoter sequence; d, part of an FNR-binding site. Intergenic-sequence hairpin structures are also indicated (for details, see panel B), as well as positions and directions of putative ORFs, labeled 1 to 3, downstream of hupL. Note the presence of xisC and the subsequent rearrangement within hupL in Anabaena strain PCC 7120. (B) hupSL intergenic sequence hairpin structures. The stop codon of hupS and the start codon of hupL are boxed, and calculated ΔG values for each hairpin structure are shown below the respective structures (112).