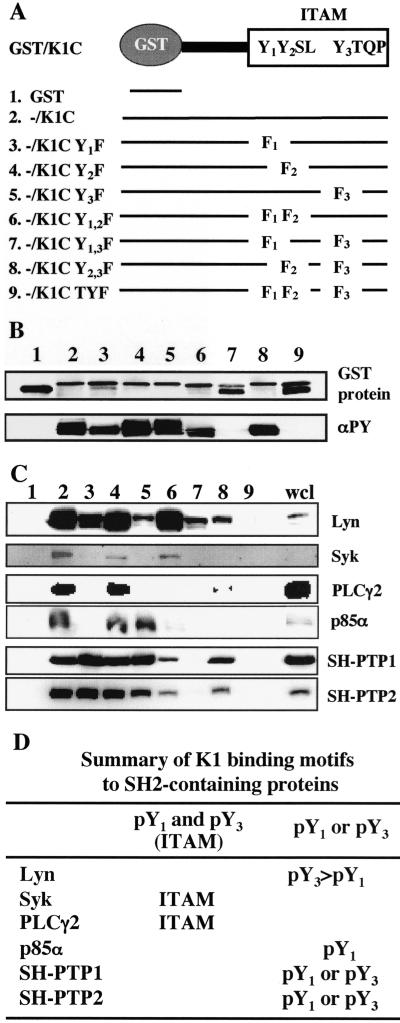
FIG. 2.
Mapping the binding sites in K1 ITAM. (A) Summary of mutant constructs. Three tyrosine residues in K1 ITAM were singly, doubly, or triply mutated to phenylalanine and fused to a pGEX4T-1 fusion construct. (B) GST/K1-C fusion proteins and their tyrosine phosphorylation. GST/K1-C constructs were transformed into E<. coli DH5α or TKX. After purification, GST, GST/K1-C, and GST/K1-C mutant proteins were detected by Coomassie blue staining (top) and their tyrosine phosphorylation was detected by immunoblotting with antiphosphotyrosine (αPY) antibody 4G10 (bottom). (C) Binding of GST/K1-C(P) fusion protein to cellular SH2-containing proteins. Phosphorylated GST/K1-C(P) fusion proteins were mixed with precleared BJAB cell lysates and subjected to immunoblotting with specific antibodies against SH2-containing signaling proteins. wcl, whole cell lysate. (D) Summary of K1 WT and mutant binding to cellular SH2-containing proteins.