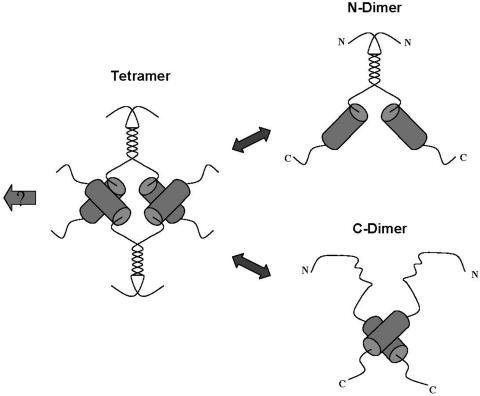
FIG. 9.
Model of VP22 oligomerization states. Based on the results from size fractionation experiments and analysis of subregions of the protein, VP22 is illustrated as a tetramer, having dimerization interfaces within the N-terminal and C-terminal regions. Dissociation of the tetramer leads to dimers, which for the full-length protein could formally be composed of dimers held together by interactions at either interface. The conserved core region and interface at the N terminus are not designed to indicate a particular structure, though computer algorithms predict alpha-helix formation within the C-terminal domain of the protein, as discussed in the text. The arrow to the left indicates the possibility that VP22 tetramers are further recruited into higher-order complexes, as discussed in the text.