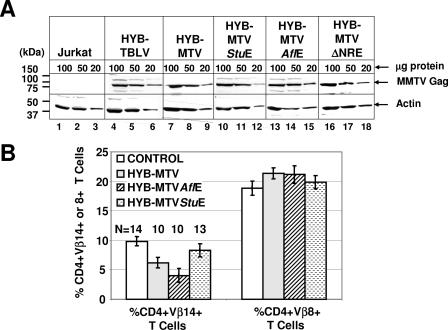
FIG. 2.
Protein expression and Sag-mediated deletion induced by wild-type MMTV and mutant viruses. (A) Western blot analysis comparing viral Gag expression levels in Jurkat T cells expressing wild-type (Jurkat/HYB-MTV) or mutant (Jurkat/HYB-MTVStuE, Jurkat/HYB-MTVAflE, and Jurkat/HYB-MTVΔNRE) MMTV proviruses. Stably transfected Jurkat cells were derived by electroporation with the appropriate proviral constructs carrying the hygromycin resistance cassette, followed by growth selection in 250 μg/ml hygromycin. Three different amounts (100, 50, and 20 μg) of whole-cell lysates were analyzed on 8% sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing polyacrylamide gels. The Gag precursor (arrow) was detected with an MMTV capsid-specific monoclonal antibody (17) using a protocol described previously (15). The same amounts of cellular lysates were incubated with antibodies specific for actin as a control for protein loading. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of Sag-mediated peripheral deletion of T cells. Injected mice were analyzed at 3 months after injection with Jurkat T cells stably expressing wild-type or mutant MMTV proviruses. CD4+ Vβ14+ and CD4+ Vβ8+ peripheral T cells were detected using phycoerythrin-conjugated anti-mouse CD4 monoclonal antibody (RM4-5) and fluorescein-conjugated anti-mouse TCR Vβ14 (14-2) or Vβ8.1 and 8.2 (MR5-2) monoclonal antibodies from Pharmingen (San Diego, Calif.). The cells were analyzed using a FACSCalibur (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, N.J.) and CELLQuest software. The percentages of TCR Vβ+ cells in the gated CD4+ T-cell populations were calculated. The number of animals (N) analyzed from each group is indicated above each bar. The mean percentage (±standard deviation) of CD4+ TCR Vβ+ T cells in each group is shown.