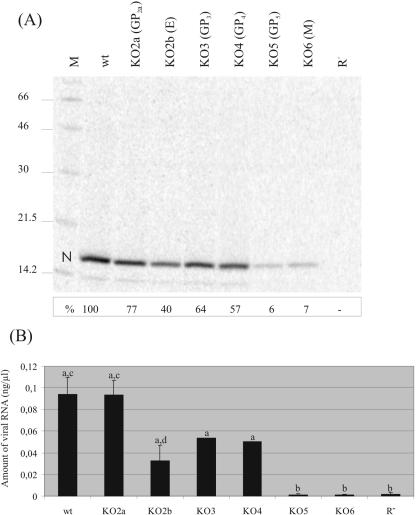
FIG. 2.
Presence of virus-like particles in transfection supernatants. (A) Immunoprecipitation analysis of recombinant viruses. BHK-21 cells were transfected with in vitro transcripts of the full-length constructs and labeled with Tran[35S] label. Virus-like particles in the culture supernatants of the transfected cells were concentrated by sedimentation through a sucrose cushion. Pellets were dissolved in PBS-TDS and subjected to immunoprecipitation with a MAb directed against the N protein. The immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed in an SDS-12% polyacrylamide gel. “N” indicates the position of the nucleocapsid protein. At the left, the positions and sizes (kilodaltons) of the molecular mass marker proteins run in parallel (lane M) are shown. BHK-21 cells transfected with replication-negative mutant R− were used as a negative control. The intensities of the N-protein bands were quantified using ImageQuant5.1 image analysis software. The values (in percentages of wt) are shown below the respective N-protein bands. (B) Quantification of relative amounts of viral RNA. BHK-21 cells were transfected with full-length RNA transcripts. At 24 h posttransfection, culture supernatants were harvested, viral RNA was isolated, and a real-time RT-PCR was performed. Shown are the mean values of two (KO3 and KO4) or four (wt, KO2a, KO2b, KO5, KO6, and R−) experiments. A statistically significant difference (P ≤ 0.05) was observed between wt/KO2a/KO2b/KO3/KO4 jointly on the one hand and KO5/KO6/R− jointly on the other hand (“a” versus “b”). In addition, a statistically significant difference (P ≤ 0.05) was observed between viral RNA levels obtained for wt and KO2a compared to KO2b (“c” versus “d”).