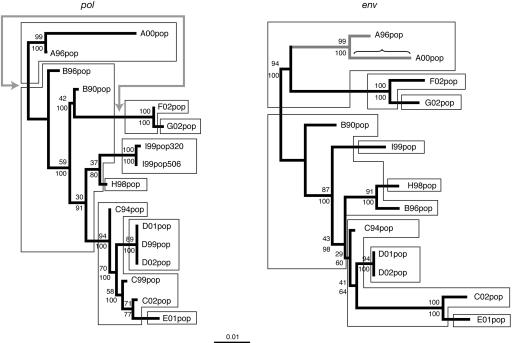
FIG. 3.
Phylogenetic trees inferred for the pol and env gp41 gene regions. Maximum likelihood and Bayesian methods resulted in the same topology for each gene region. Both trees are represented on the same scale and rooted at the position that does not distinguish between patient A and patient B as the original donor for this transmission chain. The most likely host transmission scheme is superimposed onto the viral evolutionary history: hosts are separated arbitrarily along the branch between donor and recipient. For isolates C99pop, D99pop, and I99pop320, not enough sample was left to perform env gp41 sequencing. The upper numbers at the nodes indicate the percentage of bootstrap samples, based on 1,000 replicates, in which the node is supported. The lower numbers at the nodes represent approximate posterior probabilities obtained from a posterior sample of trees. The arrow in gray indicates the branch swapping that would make the pol phylogeny topologically congruent with the known transmission history. The branch set tested to be under positive selective pressure is indicated in gray in the env gp41 tree; the branch tested to have a higher nucleotide substitution rate is indicated with the horizontal bracket.