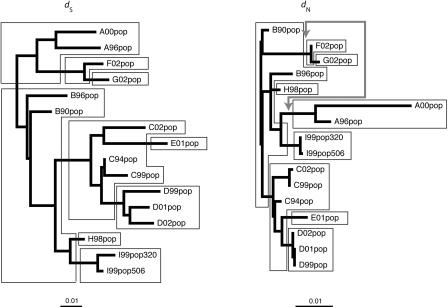
FIG. 4.
Phylogenetic trees reconstructed using synonymous (dS) and nonsynonymous (dN) distances for pol. Both trees are represented as rooted at the position that does not distinguish between patient A and patient B as the original donor for this transmission chain. The most likely host transmission scheme is superimposed onto the viral evolutionary history. The arrow in gray indicates the branch swapping that would make the dN phylogeny topologically congruent with the known transmission history.