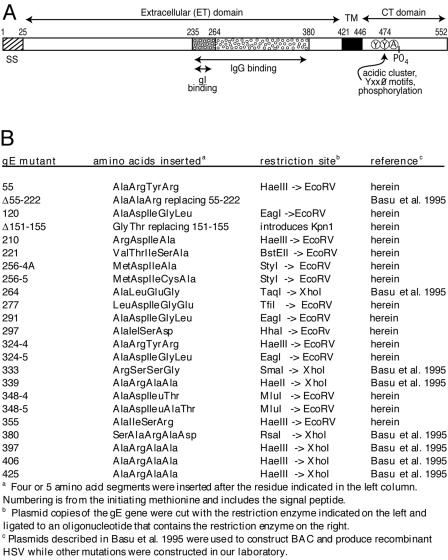
FIG. 1.
Cartoon of HSV-1 gE and description of gE ET domain mutants. (A) HSV gE is a type 1 membrane glycoprotein with a 25-amino-acid signal sequence (SS), a 396-residue extracellular (ET) domain, a 25-amino-acid transmembrane (TM) domain, and a 106-residue cytoplasmic (CT) domain that contains acidic cluster residues, YXXØ motifs, and phosphorylated residues. The ET domain contains a region from positions 235 to 380 that is necessary for binding IgG as well as a region (positions 235 to 264) that is important for binding gI (3). Note that the numbering of gE residues here refers to the HSV-1 17 strain, whereas HSV-1 F strain gE has two additional residues (58). (B) Mutations in the ET domain were constructed by inserting the indicated amino acid sequences (four or five amino acids) directly following the residue indicated. In mutant Δ55-222 a large fragment was replaced by three amino acids, and in Δ151-155, five residues were removed and two were inserted. herein, plasmids containing gE mutations constructed in this study; Basu et al. 1995, plasmids constructed by Basu et al. (3).