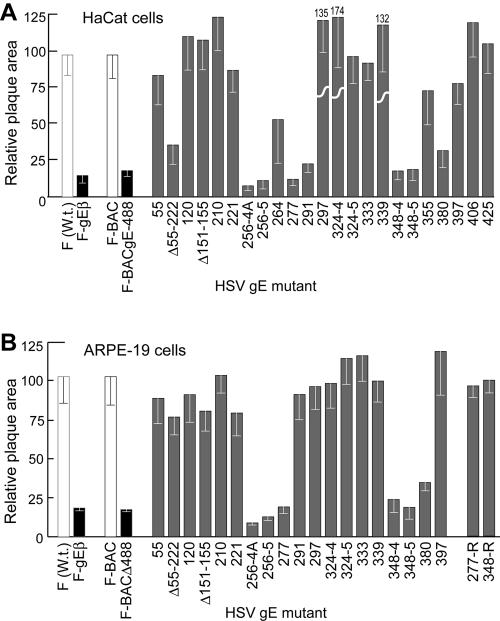
FIG. 2.
Cell-to-cell spread of HSV gE ET domain mutants in HaCaT and ARPE-19 cells. Human HaCaT keratinocytes or retinal epithelial ARPE-19 cells were infected with wild-type HSV-1 strain F or F-gEβ (derived from F), F-BAC, or F-BACgE448, which lacks all but 3 residues of the gE CT domain (derived from F-BAC), or gE ET mutants at low multiplicities. After 2 days, the cells were stained with anti-HSV polyclonal antibodies, peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies, and substrate to reveal HSV-infected cells. Ten plaques were photographed, and NIH Image software was used to calculate plaque areas. The area of wild-type F [F (W.t.)] plaques was arbitrarily set at a value of 100 for comparison with F-gEβ (derived from F), and the area of F-BAC plaques was arbitrarily set at 100 for comparison with gE ET domain mutants and F-BACΔ488 (all derived from F-BAC). Mutant 324-4 produced plaques that were 174% of the area of F-BAC plaques. 277-R and 348-4R were rescued versions of gE ET mutants 277 and 348-4, respectively.