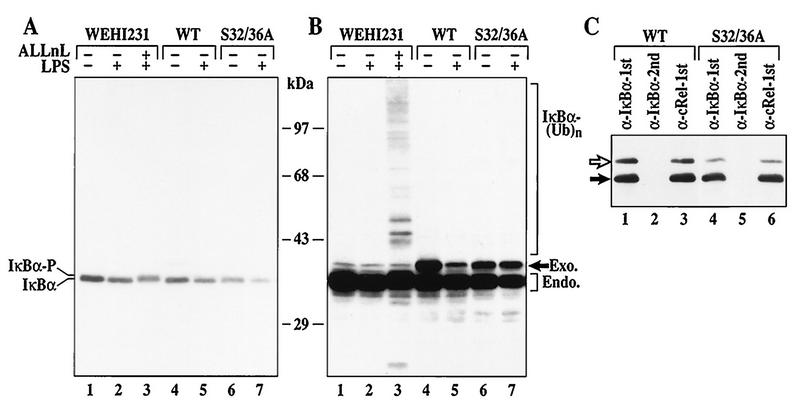
FIG. 5.
Inducible IκBα degradation requires the S32/36 phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in WEHI231 cells. (A) IκBα degradation induced by LPS in control, WT, or S32/36 WEHI231 cells. WEHI231 cells were treated with LPS (10 μg/ml) for 30 min with (lane 3) and without (other lanes) 30-min pretreatment with ALLnL (50 μg/ml). Similar numbers of cells stably expressing either WT or S32/36A mutant IκBα were also stimulated with LPS as described above. Hyperphosphorylated IκBα (IκBα-P) is shown in lane 3. (B) Longer exposure of the blot in panel A. A high-molecular-weight ladder and a smaller antiserum-reactive band are seen in lane 3. WT IκBα is degraded (compare lanes 4 and 5, band labeled Exo.), while S32/36A is not (lanes 6 and 7). (C) Both exogenous and endogenous IκBα are complexed with c-Rel in WEHI231 cells. WEHI231 cells expressing WT (lanes 1 to 3) or S32/36A (lanes 4 to 6) were processed for coimmunoprecipitation as described in legend to Fig. 1D. The positions of exogenous (open arrow) and endogenous (filled arrow) proteins are shown on the left.