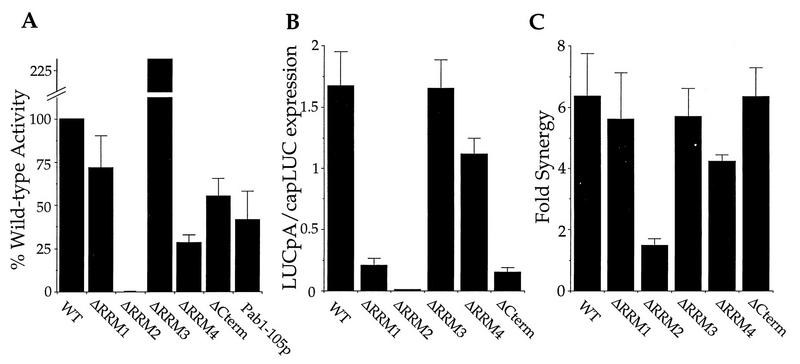
FIG. 4.
RRM2 is required for poly(A) tail-dependent translation in vitro. (A) Reconstitution of translation in Pab1p immunoneutralized extracts with the recombinant Pab1p variants and LUCpA mRNA. The percentage of reconstitution, relative to the wild type (WT), achieved by the addition of the indicated Pab1p variants to the immunoneutralized extract is plotted on the y axis. Values given are the averages of multiple experiments with three different extracts. Each protein was tested over a range of concentrations, and the maximal activation value was used to represent the percent reconstitution. On average, a nonneutralized extract gave 150 U of luminescence in the absence of added protein, and a neutralized extract gave 2.2 U of luminescence. (B) Poly(A) tail-dependent translation in extracts containing different Pab1p variants. Extracts from yeast strains harboring the indicated Pab1p were prepared and assayed for the indicated LUC mRNA translation. Values on the y axis represent the ratio of LUCpA translation to capLUC translation. The translation of capLUC mRNA serves as an internal standard to control for variation in the overall translational activity of each extract. (C) Synergistic activation of translation in extracts containing different Pab1p variants. The ratio of the amount of translation of capLUCpA mRNA to the sum of capLUC and LUCpA mRNA translation [capLUCpA/(capLUC + LUCpA)] within the indicated extract is plotted on the y axis. For panels B and C, the plotted ratios represent the average of at least two experiments with each of two independently prepared extracts. Representative luminescence values for capLUC mRNA translation in each extract were as follows: WT, 39.8; ΔRRM1, 20.3; ΔRRM2, 23.4; ΔRRM3, 79.8; ΔRRM4, 29.4; and ΔCterm, 5.8.