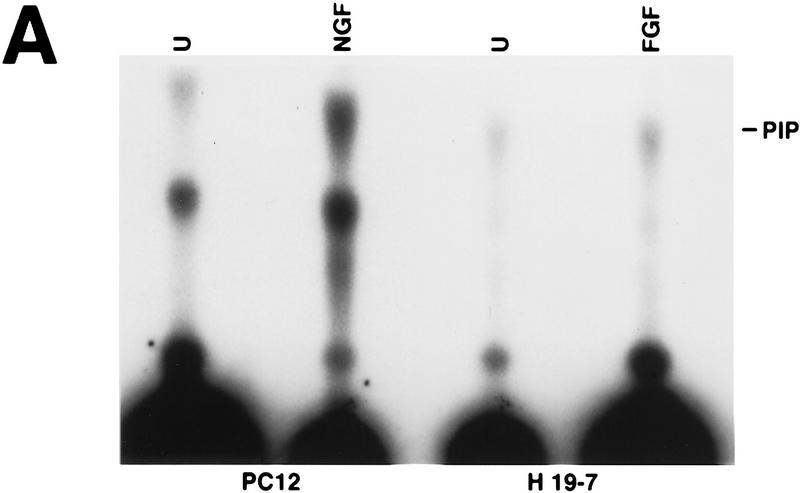
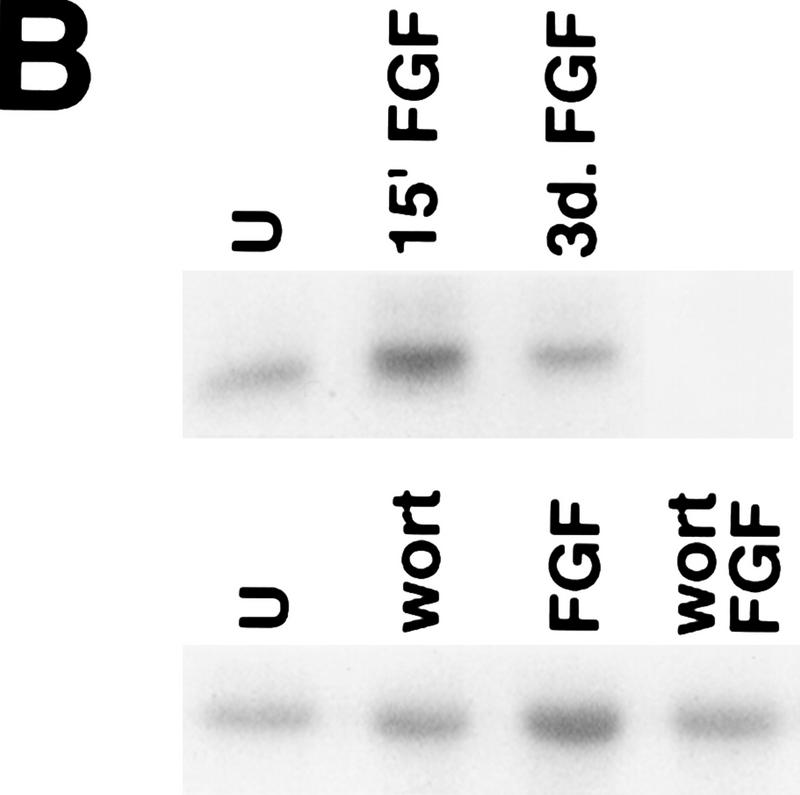
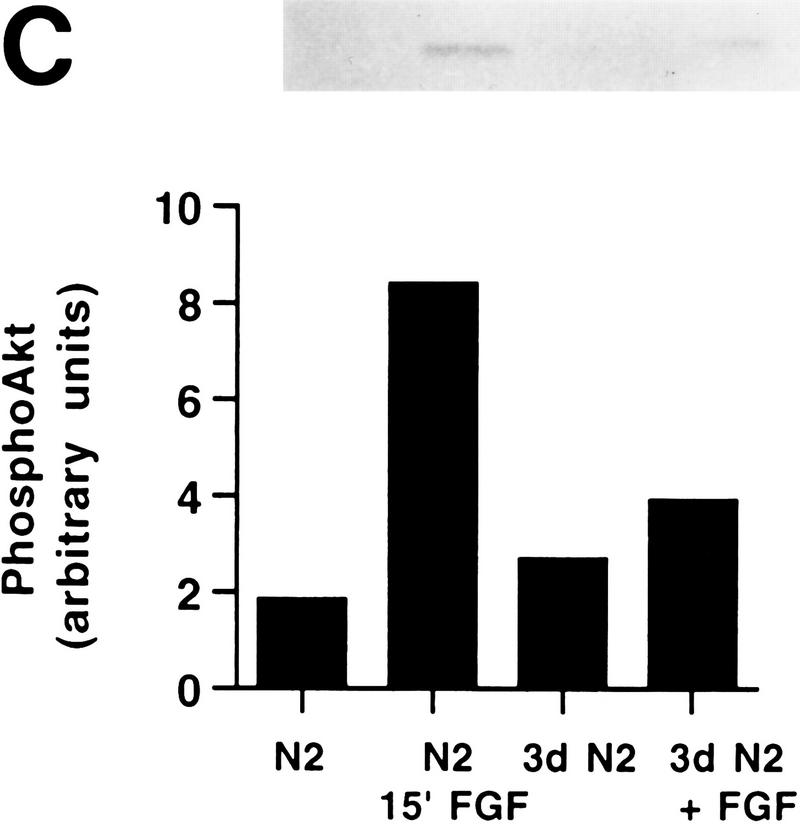
FIG. 2.
PI 3-kinase and Akt activities in H19-7 cells. (A) Stimulation of PI 3-kinase activity by differentiation factors in H19-7 and PC12 cells. The cells were either untreated (U) or treated for 1 min with 10 ng of FGF per ml or 100 ng of NGF per ml. PI 3-kinase was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with antiphosphotyrosine antibody and assayed for PI 3-K activity as described in Materials and Methods. The position of the PI 3-kinase product, PI 3-phosphate, is indicated (PIP). (B) (Upper panel) Stimulation of Akt activity by FGF in H19-7 cells. H19-7 cells were cultured in N2 medium at 39°C for 24 h and then untreated (U), treated for 15 min (15′ FGF), or differentiated for 3 days (3d. FGF) with 10 ng of FGF per ml. Endogenous Akt was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates and assayed by phosphorylation of a pseudosubstrate peptide as described in Materials and Methods. (Lower panel) Inhibition of FGF activation of Akt by wortmannin. Cells were cultured in DMEM at 39°C for 24 h and then untreated (U) or pretreated with 200 nM wortmannin (wort) for 10 min. In some samples, 10 ng of FGF per ml was added to untreated (FGF) and wortmannin-pretreated (wort FGF) cells, which were then incubated for 15 min. Akt activity was assayed as described above. These results are representative of two independent experiments. (C) Transient phosphorylation of Akt during H19-7 differentiation. Whole-cell extracts from cultures treated without FGF (N2) or with FGF for 15 min (15′) or 3 days (3d) were probed with an antibody specific for phosphorylated Akt (inset). The phosphorylated Akt bands were quantified by optical densitometry and normalized to the amounts of Akt protein detected on the same blot with the phosphorylation state-independent antibody (see Materials and Methods). These results are representative of three independent experiments.