FIG. 2.
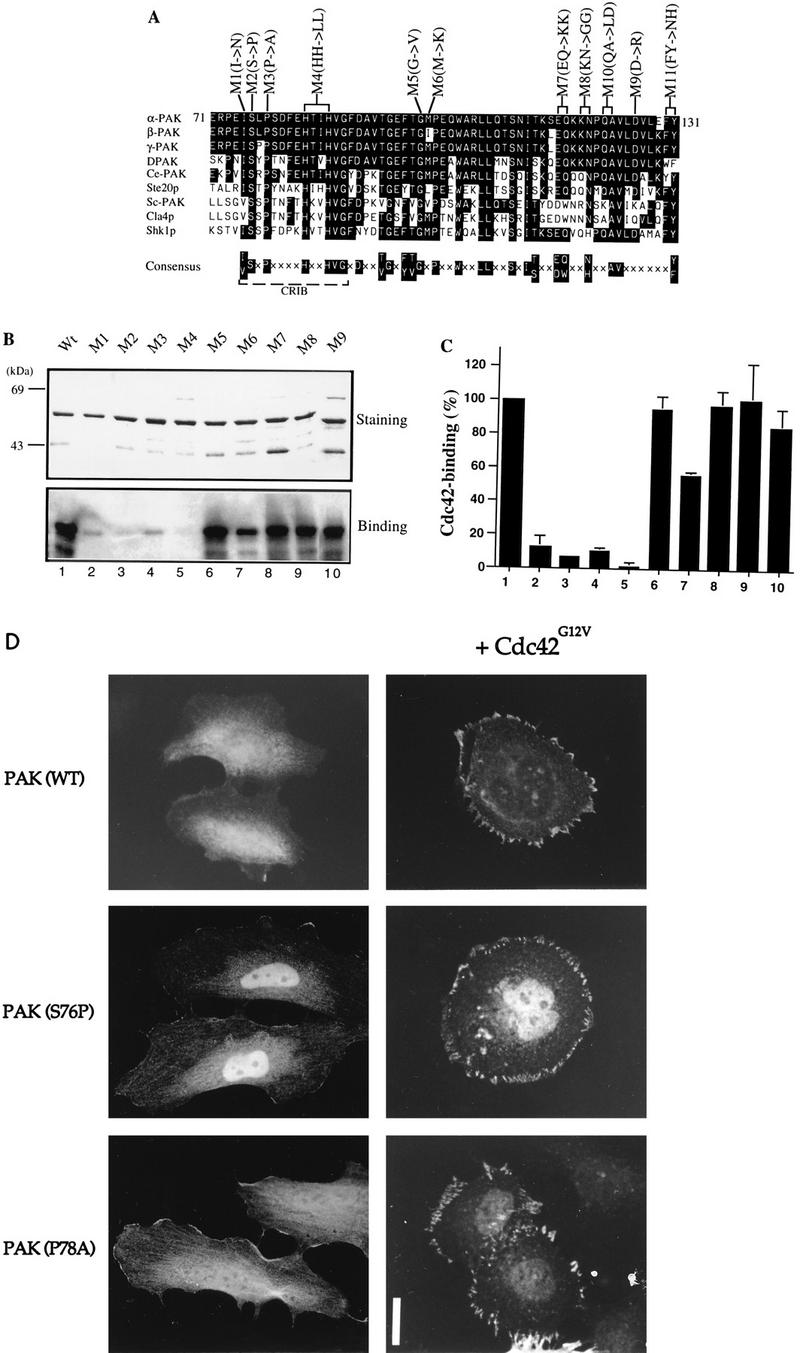
Mutations in the N terminus of the PAN motif abolish p21 binding. (A) Sequence alignment of PAN motifs of PAK-related proteins from rat (α-, β-, and γ-PAK), Drosophila (DPAK), Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce-PAK), S. cerevisiae (Ste20p, Cla4p, and Sc-PAK), and Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Shk1p). Accession numbers are given elsewhere (27). The conserved residues are boxed in black, and a consensus of these is shown below. Amino acid substitutions corresponding to each of the mutant constructs are shown. (B) The first 250 amino acids of each αPAK mutant and wild-type (Wt) construct were purified as GST fusion proteins, and 1 μg of each protein was resolved by SDS-PAGE (11% gel) and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (top); p21 binding to bands containing 0.4 μg of each protein was determined by overlays with [γ-32P]GTP-Cdc42 (bottom). (C) The Cdc42 binding signals in panel B (bottom) were quantified on a PhosphorImager; the means of two independent experiments are shown. (D) Expression constructs encoding HA-αPAK mutants as indicated were transfected into HeLa cells alone or with FLAG-Cdc42G12V. Typical cells stained for αPAK are shown; in all cases, the cells were also stained with antipaxillin to confirm that peripherally located PAK was in FCs. Bar, 10 μm.
