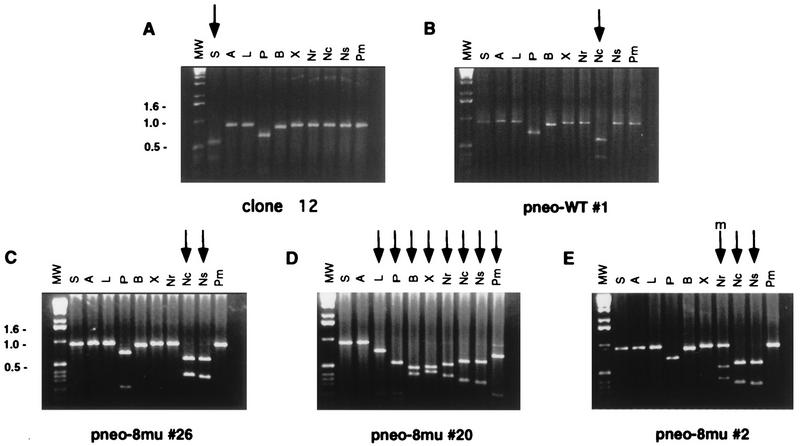
FIG. 4.
PCR analysis of parental ES cells and neo+ clones derived from cotransfection of pneo substrates with the I-SceI expression vector. The neo gene coding region was amplified by PCR as a 0.9-kb fragment from genomic DNA with primers Neo1 and Neo2 and electrophoresed on agarose gels following digestion by the indicated endonucleases. Endonucleases are abbreviated as follows: I-SceI, S; ApaI, A; ApaLI, L; PstI, P; BamHI, B; XbaI, X; NruI, Nr; NcoI, Nc; NsiI, Ns; and PmlI, Pm. The 1-kb ladder molecular weight marker used is also indicated (MW). Note that due to naturally occurring PstI and BamHI sites (Fig. 2), the amplified fragments in each of the clones are shifted when cut with these enzymes. (A) Amplified fragment from the S2neo gene in the parental ES clone 12 cells. The fragment is cleaved by I-SceI, as expected, but it is not cleaved by NcoI or the restriction enzymes whose sites were created in the pneo plasmids. (B) Amplified neo fragment from a neo+ colony from cotransfection of pneo-WT and the I-SceI expression vector. The fragment is cleaved by NcoI but not by I-SceI or the other restriction enzymes. (C to E) Amplified neo gene fragments from selected neo+ colonies from cotransfection of the pneo-8mu substrate and the I-SceI expression vector, showing a short gene conversion tract (C), a long tract (D), and a mixed tract (E). The amplified fragment from each of the neo+ clones is not cleaved by I-SceI but is cleaved by NcoI and various restriction enzymes, as indicated by the arrows. In clone pneo-8mu #20 (D), the small amount of DNA not cleaved by PmlI is not reproducible. The “m” over the arrow in panel E indicates partial cleavage by the restriction enzyme.