Table 1.
The list of chemical structure of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) monomers introduced in this article [[8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18], [19], [20], [21], [22], [23], [24], [25]].
| TCM monomer | Chemical structure | Refs. |
|---|---|---|
| Pal | 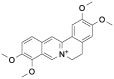 |
[8] |
| Ber | 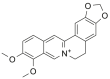 |
[8,9] |
| Cory-B | 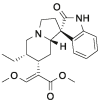 |
[10] |
| Hed | 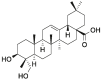 |
[11] |
| Nef | 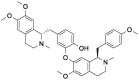 |
[11] |
| Bai | 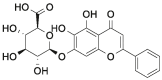 |
[11,12] |
| Cur | 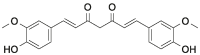 |
[[13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18], [19], [20]] |
| ECG | 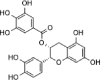 |
[21] |
| RSV | 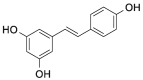 |
[22] |
| Que | 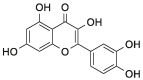 |
[23] |
| DHT | 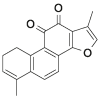 |
[24] |
| SAB |  |
[25] |
| CPT | 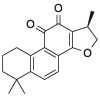 |
[25] |
Pal: palmatine; Ber: berberine; Cory-B: corynoxine-B; Hed: hederagenin; Nef: neferine; Bai: baicalin; Cur: curcumin; ECG: epicatechin gallate; RSV: resveratrol; Que: quercetin; DHT: dihydrotanshinone; SAB: salvianolic acid B; CPT: cryptotanshinone.
