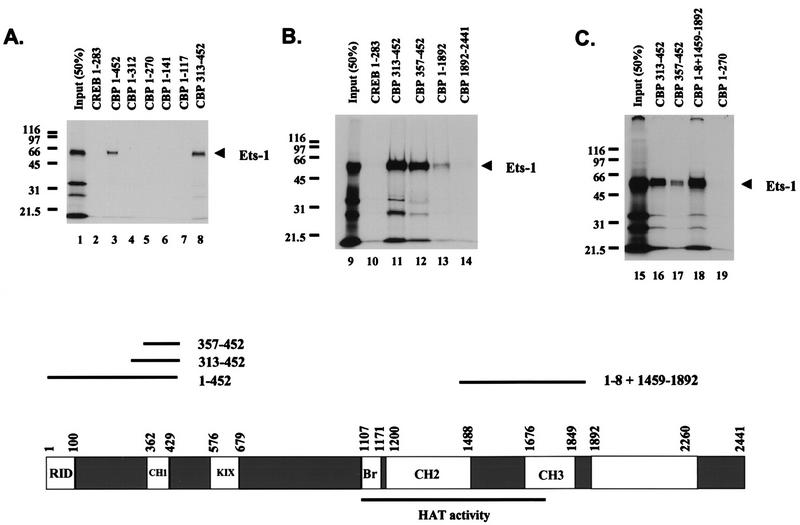
FIG. 5.
Ets-1 binds at least two separate regions of CBP in vitro. Shown are the results of three separate experiments demonstrating specific Ets-1 binding sites on CBP. GST-CBP pull-down experiments were performed with [35S]methionine-labeled Ets-1 produced in vitro and GST-CBP fusion proteins purified from E. coli. Molecular mass markers are indicated (in kilodaltons). Input (50%) shows 50% of the Ets-1 used in each pull-down assay. GST CREB 1–283 (CREB 1–283) is GST fused to CREB aa 1 to 283 and acts a negative control for Ets-1 binding. Comparable amounts of GST fusion proteins were used in each assay. A scale drawing depicting the CBP domain structure, along with approximate domain boundaries in residues from the N terminus (position 1) to the C terminus (position 2441) is shown at the bottom. The receptor interaction domain (RID), the three cysteine-plus histidine-rich domains (CH1, CH2, and CH3), the CREB binding KIX domain (KIX), and the bromodomain (Br) are shown (6, 19, 22, 36, 58). CBP residues 1099 to 1758 sufficient for HAT activity are underlined (11). Also shown are scale-drawn lines corresponding to CBP fragments with inclusive endpoints sufficient to bind Ets-1 when fused to GST (1 to 452, 313 to 452, 357 to 452, 1 to 8 plus 1459 to 1892) and their relative positions in CBP. This figure was produced using Macintosh versions of Adobe Photoshop and Microsoft PowerPoint. The results are representative of at least two independent experiments.