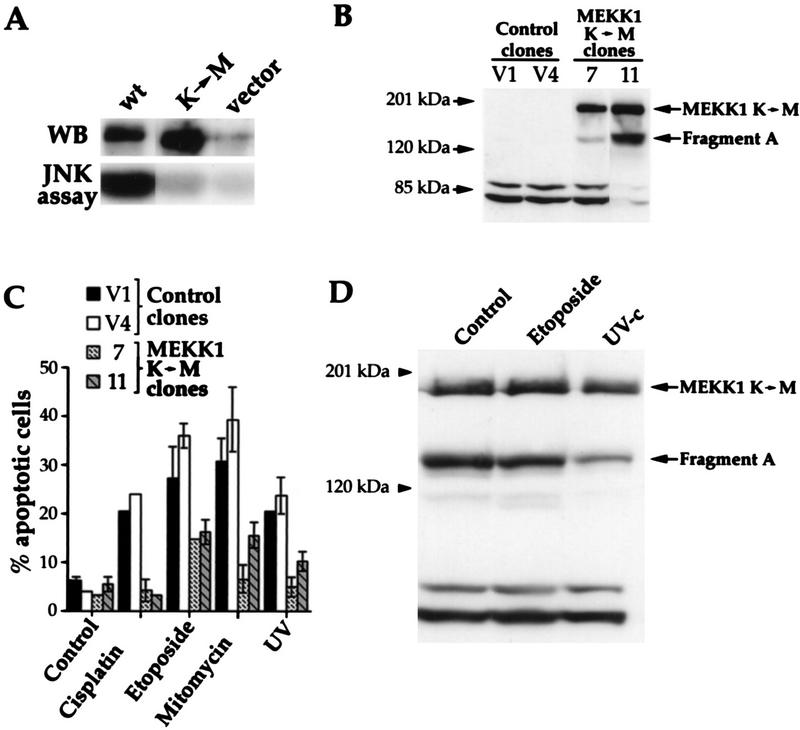
FIG. 4.
MEKK1 is involved in genotoxin-induced apoptosis. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with 4 μg of empty pcDNA3 vector or pcDNA3 containing wild-type MEKK1 (plasmid MEKK1.dn3) or the MEKK1 K(1253)→M mutant [plasmid MEKK1(−).dn3]. After 18 h, the cells were lysed and the MEKK1 proteins were immunoprecipitated with antibody 12CA5, recognizing the NH2-terminal HA tag. The immunoprecipitates were then analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with antibody 12CA5. Alternatively, the JNK activity of the cell lysates was determined as described in Materials and Methods. Despite similar levels of expression, only the wild-type MEKK1 protein was able to induce the activity of the JNK pathway. (B) Clones of HEK293 cells stably transfected with pcDNA3 (clones V1 and V4) or pcDNA3 expressing the kinase-inactive MEKK1 K(1253)→M protein [plasmid MEKK1(−).dn3] (clones 7 and 11) were lysed, and the expression of MEKK1 was determined by Western blot analysis with antibody 12CA5. The positions of the full-length kinase-inactive MEKK1 and fragment A are indicated (see the text for details about the generation of fragments A and B). (C) The clones shown in panel B were stimulated as described in the legend to Fig. 3. Apoptotic cells were scored after acridine orange staining (41). Data are the mean ± standard error of the mean for duplicate determinations. (D) Clone 11 (described in panel B) was incubated with etoposide or irradiated with UV as described in Fig. 3. The cells were lysed and then analyzed by Western blotting with anti-HA antibody 12CA5. The positions of the full-length kinase-inactive MEKK1 and fragment A are indicated.