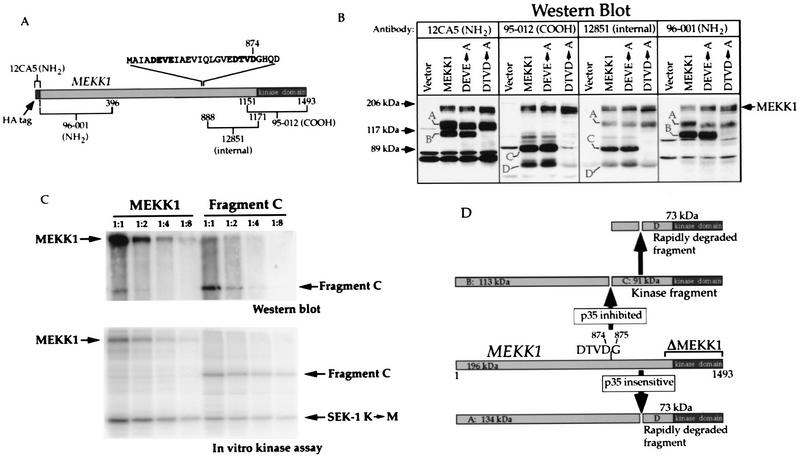
FIG. 7.
Mutation of the mouse MEKK1 sequence 871DTVD874 blocks p35-inhibited MEKK1 cleavage. (A) Schematic representation of the HA-tagged mouse MEKK1 protein showing the regions (the numbers correspond to the positions of the amino acids) used to generate the indicated antibodies. Also shown is the sequence (one-letter code) between amino acids 853 and 888 where the tetrapeptides DEVE and DTVD (in bold type) are replaced with alanine residues in mutants DEVE→A and DTVD→A, respectively. (B) Western blot analysis with the antibodies shown in panel A of lysates derived from HEK293 cells transfected with 0.5 μg of pcDNA_3.cp4, MEKK1.cp4, DEVE_A.cp4, or DTVD_A.cp4. Letters A to D indicate the same cleavage products as those shown in Fig. 6A. (C) Full-length activated MEKK1 and fragment C have similar SEK1 K→M phosphorylation activities. HEK293 cells were transfected with 4 μg of MEKK1 in pcDNA3 (MEKK1k.dn3 plasmid) or fragment C in pcDNA3 (G875.dn3 plasmid). At 18 h after transfection, 5 mg of cell lysate proteins was immunoprecipitated with antibody 12CA5 (recognizing the NH2-terminal HA tag). Serial dilutions of the immunoprecipitates (1:1, 1:2, 1:4, and 1:8) were then analyzed by Western blotting with antibody 95-012 (recognizing the COOH terminus of MEKK1) or analyzed for their ability to phosphorylate the SEK1 K→M substrate. (D) Schematic representation of p35-inhibited and p35-insensitive cleavage in the mouse MEKK1 protein. Letters A to D indicate the names of the cleavage products. The molecular masses were calculated from the migration of the markers in at least two different experiments, such as the one presented in panel B.