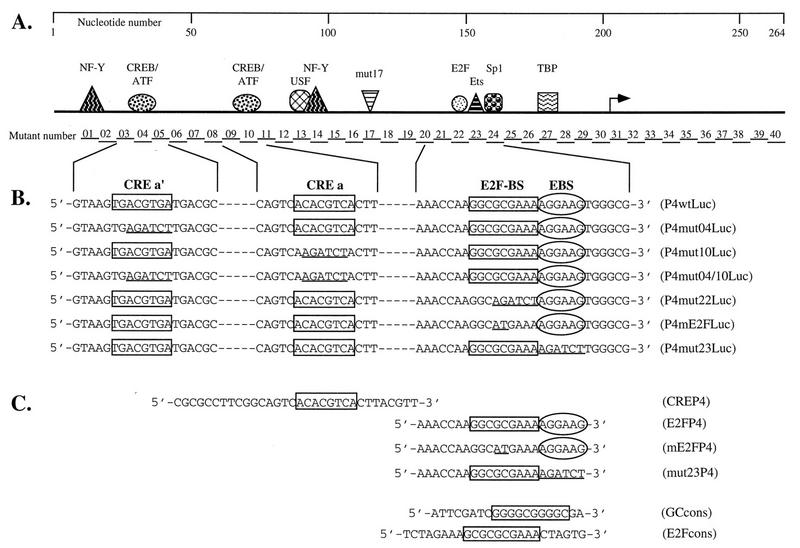
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the MVMp P4 promoter, of the mutants derived from it, and of the oligonucleotides used in this study. (A) The upper panel depicts the P4 promoter from nt 1 to the translation initiation site at nt 261 (numbering according to Astell et al. [2]). The arrow indicates the transcription initiation site. Symbols represent transcription factors shown to interact with specific P4 promoter sequence elements: TBP, TATA-box-binding protein (1, 16); Sp1, GC-box-binding proteins (1, 17); Ets, Ets family of transcription factors (17); E2F, E2F-binding-site-specific protein complexes (reference 16 and this study); mut17, as yet unidentified proteins binding to and activating promoter P4 via the DNA element mutated in P4mut17 (15); NF-Y, Y-box-binding protein (18); USF, E-box-binding protein (19); CREB/ATF, CRE-binding proteins (36). The 40 contiguous BglII substitutions introduced in mutants P4mut01 to P4mut40, respectively, are located along the promoter. (B and C) The sequence elements analyzed in this study are framed and aligned beneath the line diagram of the promoter. Underlined sequences indicate mutations introduced in the various elements. (B) P4 promoter constructs driving expression of the luciferase reporter gene. (C) Oligonucleotides used as probes or competitors in electrophoretic mobility assays.