Abstract
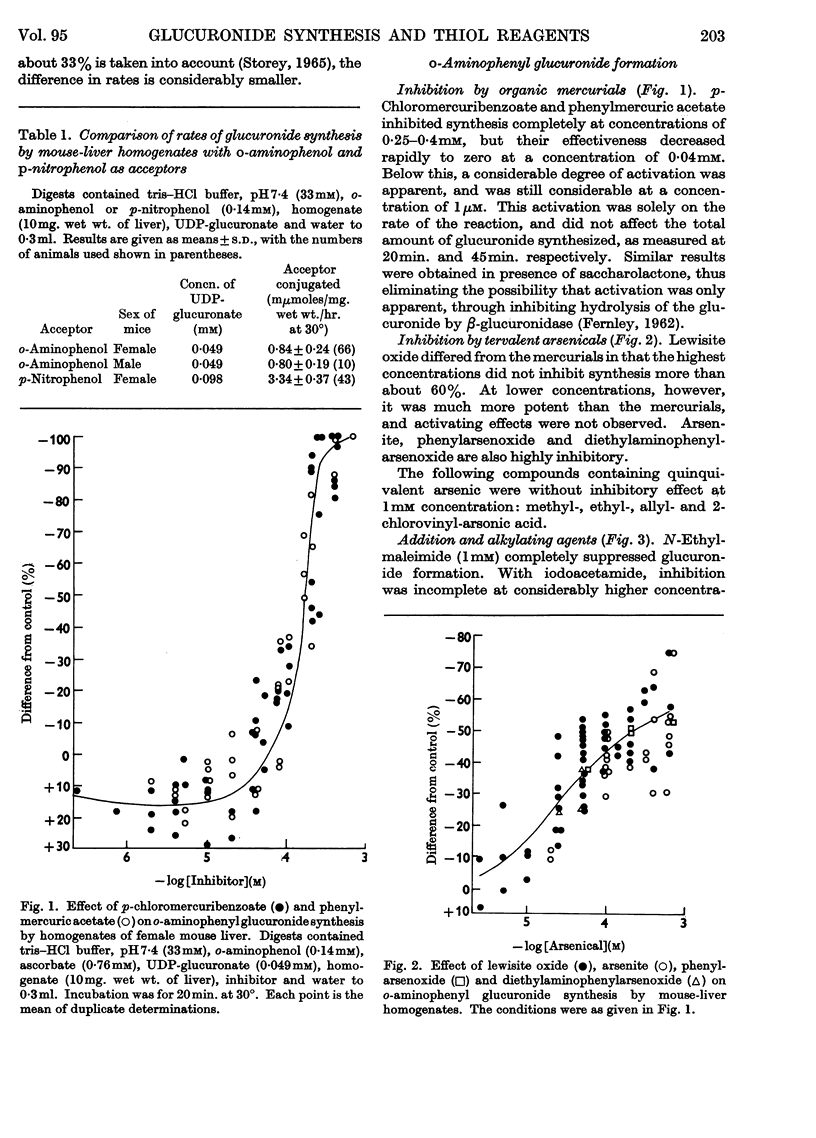
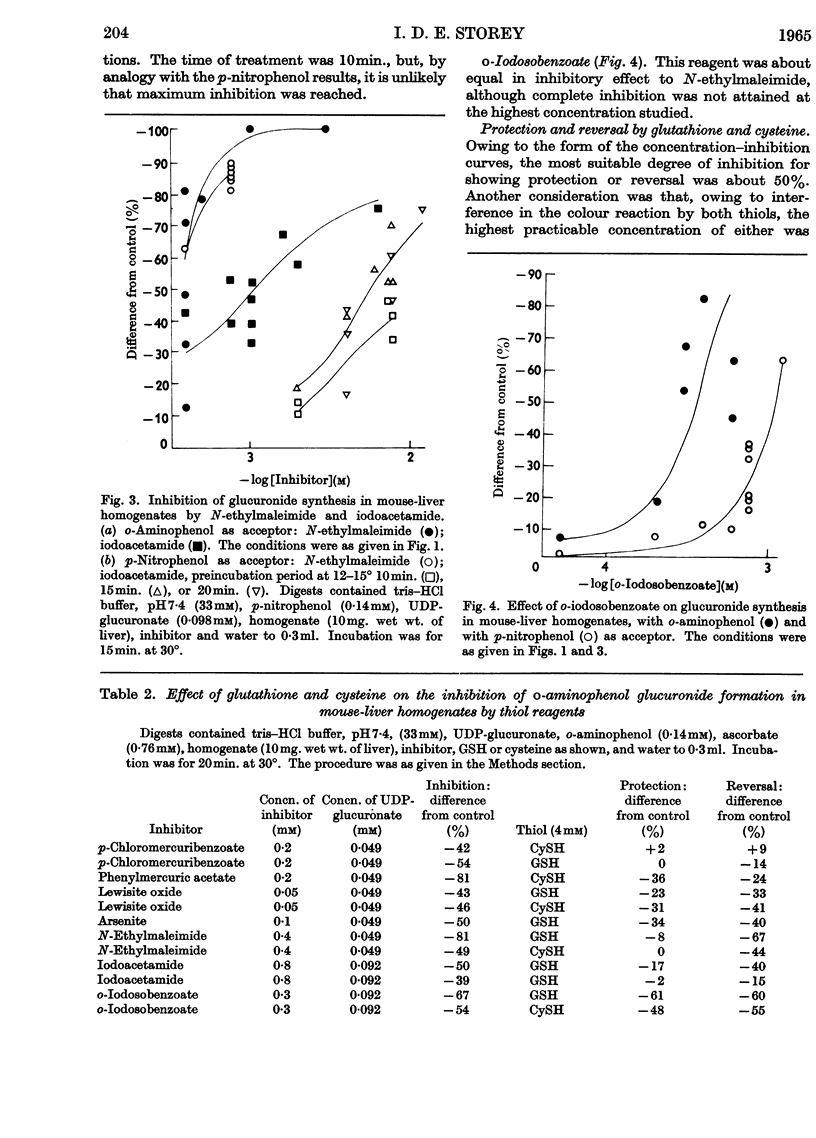
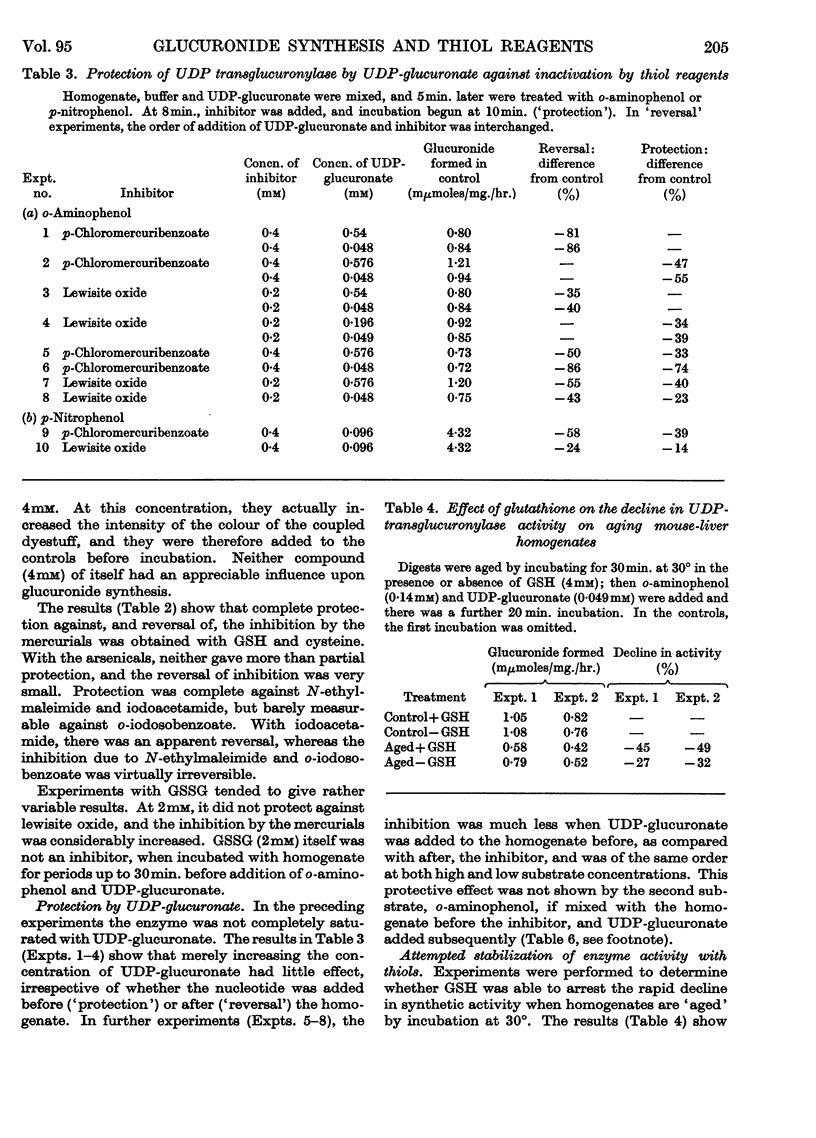
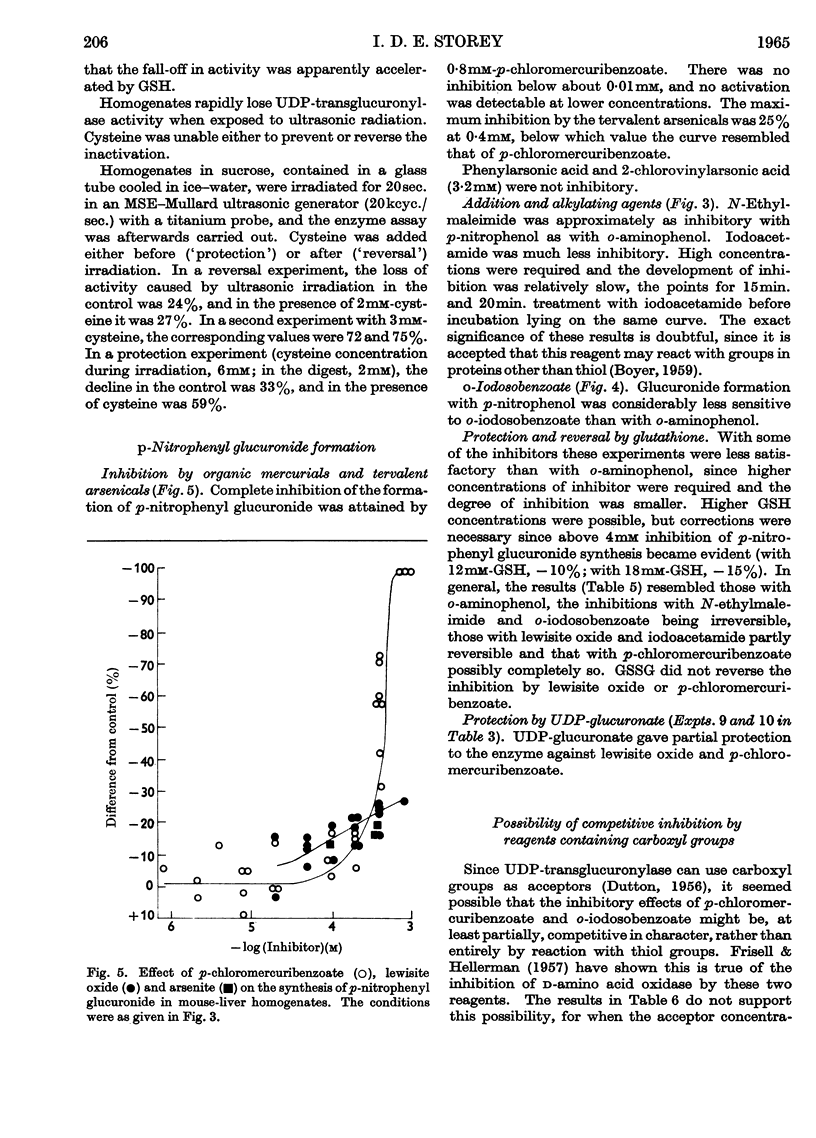
1. A study of the catalysis of the formation of the glucuronides of o-aminophenol and p-nitrophenol by the uridine diphosphate transglucuronylase of homogenates of female mouse liver has been made, with reference to the effect of reagents reacting with thiol groups. 2. The synthesis of both glucuronides was completely inhibited by organic mercurials and N-ethylmaleimide. The inhibition was only partial with arsenite and the arsenoxides, iodoacetamide and o-iodosobenzoate. 3. The o-aminophenol system was much more sensitive than that for p-nitrophenol to all the thiol reagents, except N-ethylmaleimide, which was equally active in both systems. 4. At very low concentrations of the organic mercurials, the o-aminophenol system was activated. 5. With o-aminophenyl glucuronide formation, complete protection was given by glutathione and cysteine against the organic mercurials, N-ethylmaleimide and iodoacetamide, and partial protection against the arsenicals. Reversal was complete against the mercurials, and very limited against the arsenicals and iodoacetamide. The effects of N-ethylmaleimide and o-iodosobenzoate were irreversible. Results with p-nitrophenol were very similar. 6. Uridine diphosphate transglucuronylase was partially protected against p-chloromercuribenzoate and lewisite oxide by uridine diphosphate glucuronate, but not by o-aminophenol. 7. Glutathione did not prevent the decline in the rate of conjugation of o-aminophenol when homogenates were aged by incubation at 30°. Cysteine was unable to prevent or reverse inactivation by ultrasonic radiation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELROD J., INSCOE J. K., TOMKINS G. M. Enzymatic synthesis of N-glucosyluronic acid conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):835–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTTON G. J., STOREY I. D. Uridine compounds in glucuronic acid metabolism. I. The formation of glucuronides in liver suspensions. Biochem J. 1954 Jun;57(2):275–283. doi: 10.1042/bj0570275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTTON G. J. Uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid as glucuronyl donor in the synthesis of ester, aliphatic and steroid glucuronides. Biochem J. 1956 Dec;64(4):693–701. doi: 10.1042/bj0640693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERNLEY H. N. Effects of some heavy-metal ions on purified mammalian beta-glucuronidase. Biochem J. 1962 Mar;82:500–509. doi: 10.1042/bj0820500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRISELL W. R., HELLERMAN L. The sulfhydryl character of D-amino acid oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):53–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLERMAN L., SCHELLENBERG K. A., REISS O. K. L-glutamic acid dehydrogenase. II. Role of enzyme sulfhydryl groups. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1468–1478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISSELBACHER K. J., CHRABAS M. F., QUINN R. C. The solubilization and partial purification of a glucuronyl transferase from rabbit liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3033–3036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIELLEY W. W., BRADLEY L. B. The relationship between sulfhydryl groups and the activation of myosin adenosinetriphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):653–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POGELL B. M., LELOIR L. F. Nucleotide activation of liver microsomal glucuronidation. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOREY I. D. SOME DIFFERENCES IN THE CONJUGATION OF O-AMINOPHENOL AND P-NITROPHENOL BY THE URIDINE DIPHOSPHATE TRANSGLUCURONYLASE OF MOUSE-LIVER HOMOGENATES. Biochem J. 1965 Apr;95:209–214. doi: 10.1042/bj0950209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


