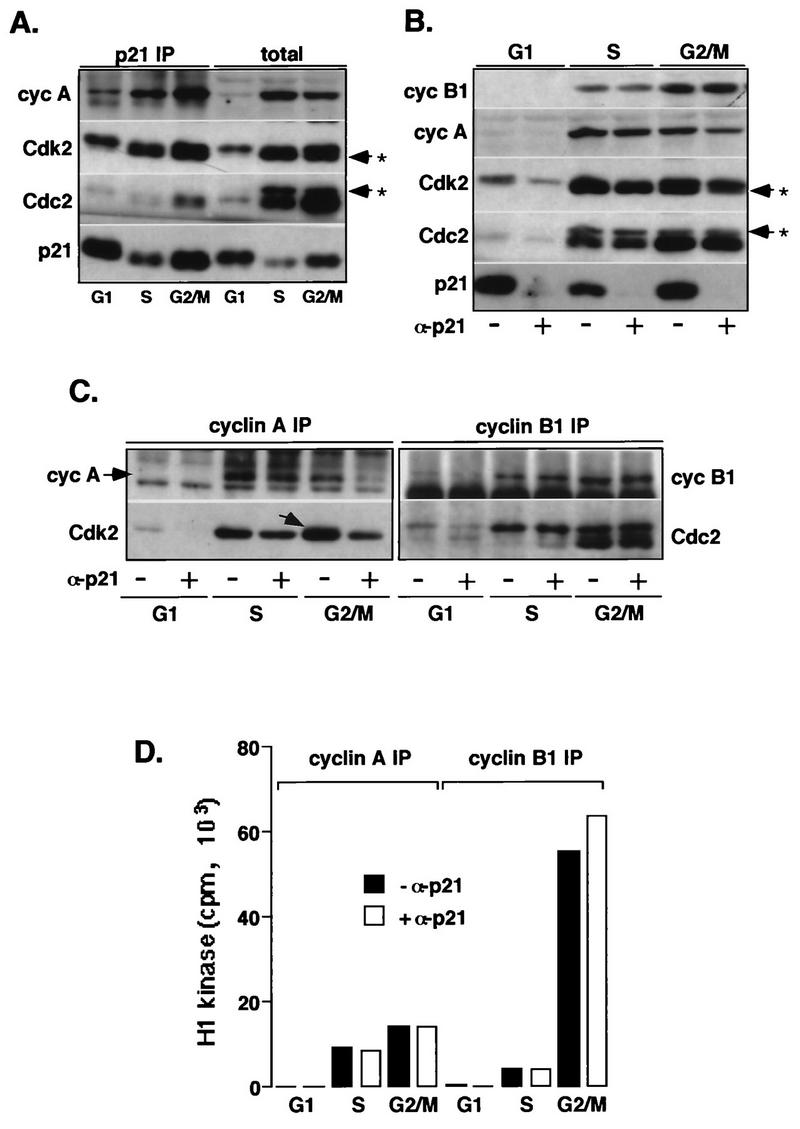
FIG. 4.
p21-associated cyclin (cyc)-Cdk2 complexes are inactive. Extracts prepared from normal fibroblasts (Hs68) synchronized in G1, S, and G2/M phases are depleted of p21. (A) Western blot analysis of p21 immunoprecipitates (IP) from the different cell extracts (200 μg) and total proteins in the corresponding lysates (40 μg). (B) Western blot analysis of total proteins in cell extracts (40 μg) depleted (+ α-p21) or not depleted (− α-p21) of p21. (C) Western blot analysis of cyclin A and cyclin B1 immunocomplexes isolated from the p21-depleted and mock-depleted extracts (150 μg). (D) Cyclin A- or B1-associated histone H1 kinase activity. In these experiments, cyclin A and cyclin B1 immunocomplexes, assayed for kinase activity by using histone H1 as a substrate, were separated by SDS-PAGE (11% gel), transferred onto an Immobilon membrane and simultaneously analyzed for the presence of cyclins and Cdks by Western blotting, and exposed to reveal histone H1-associated radioactivity. In addition, Coomassie blue-stained histone H1 bands remaining on the gel (about 50%) were excised, and associated radioactivity was analyzed by Cerenkov counting. The immunoblots were probed with indicated antibodies, except that in cyclin B1 immunoprecipitates, Cdc2 was also detected by using an anti-PSTAIRE monoclonal antibody. The extent of removal of cyclins or Cdks upon p21 depletion was evaluated by densitometric scanning of immunoblots. Note that in G2/M cells, cyclin A increasingly associates with unphosphorylated Cdk2 (indicated by an arrow in panel C). Arrows with asterisks in panels A and B indicate phosphorylated Cdk species.