Abstract
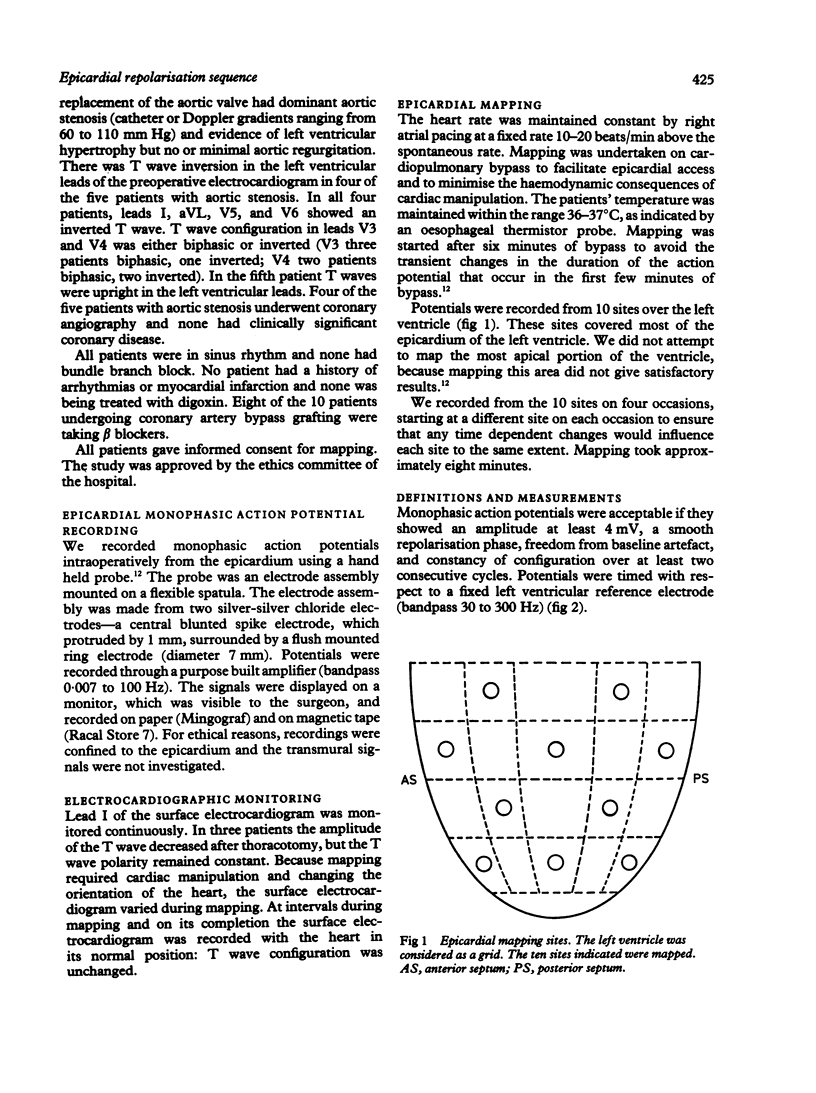
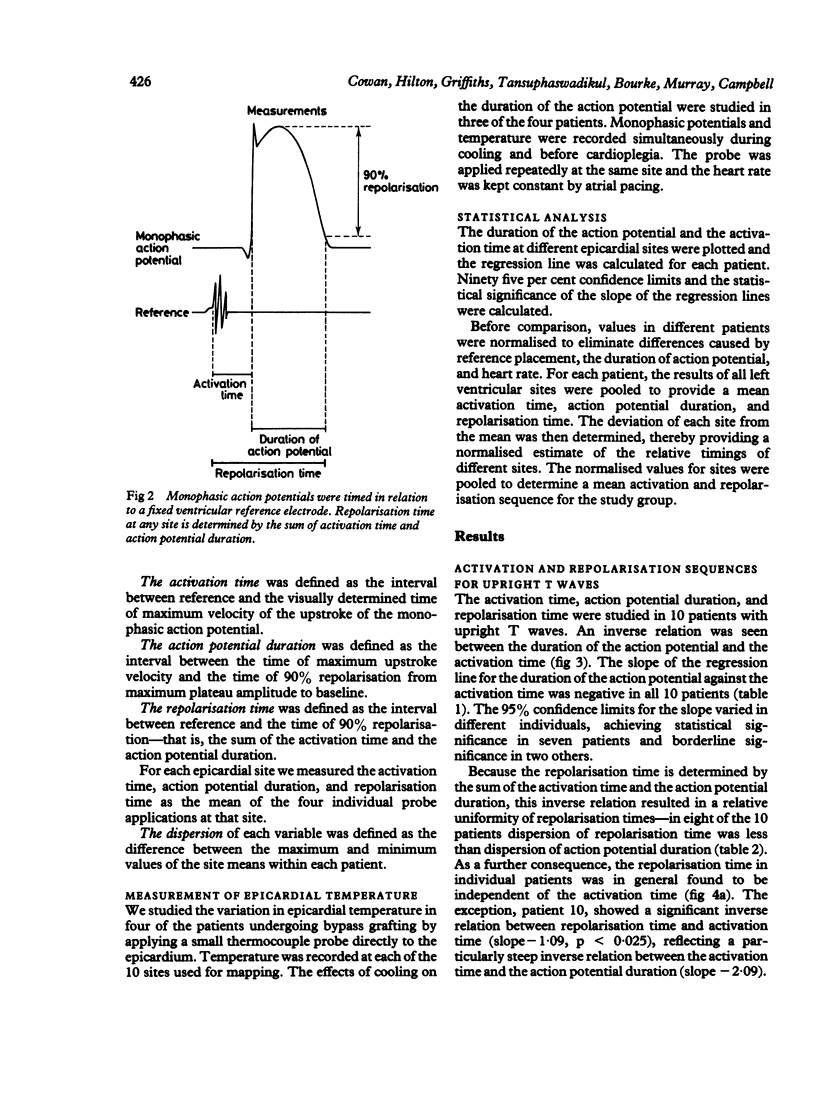
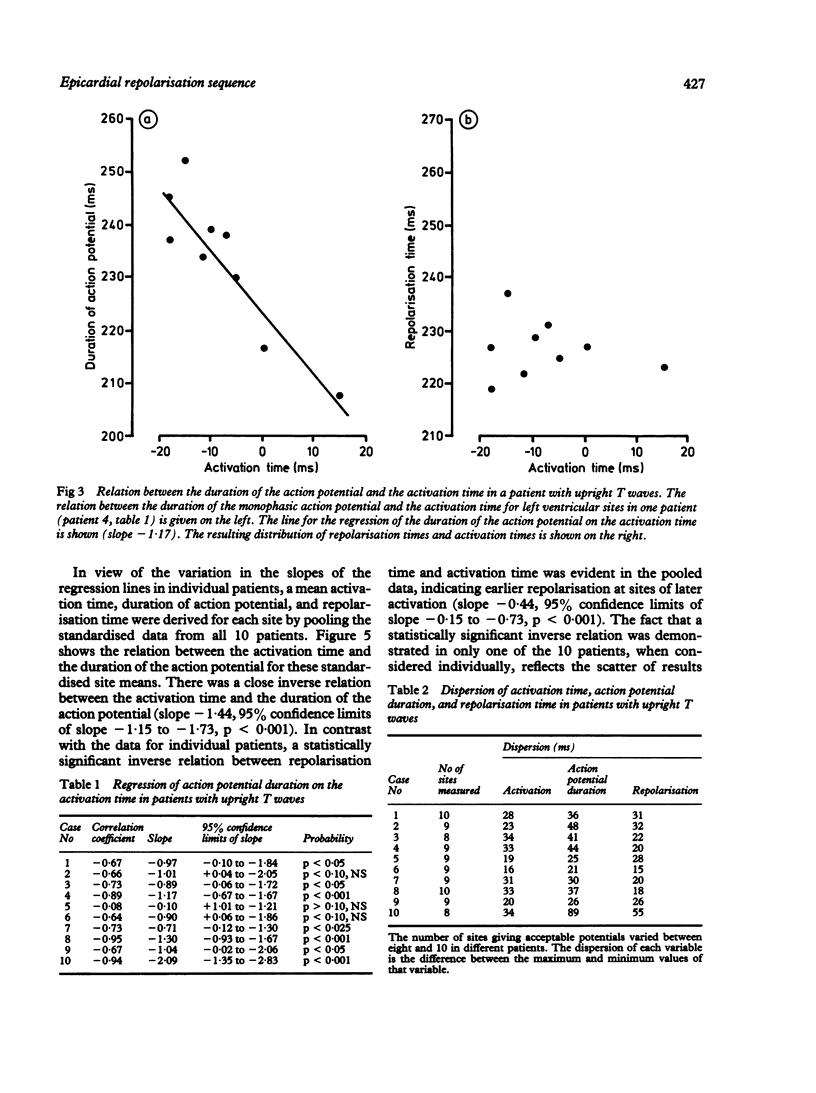
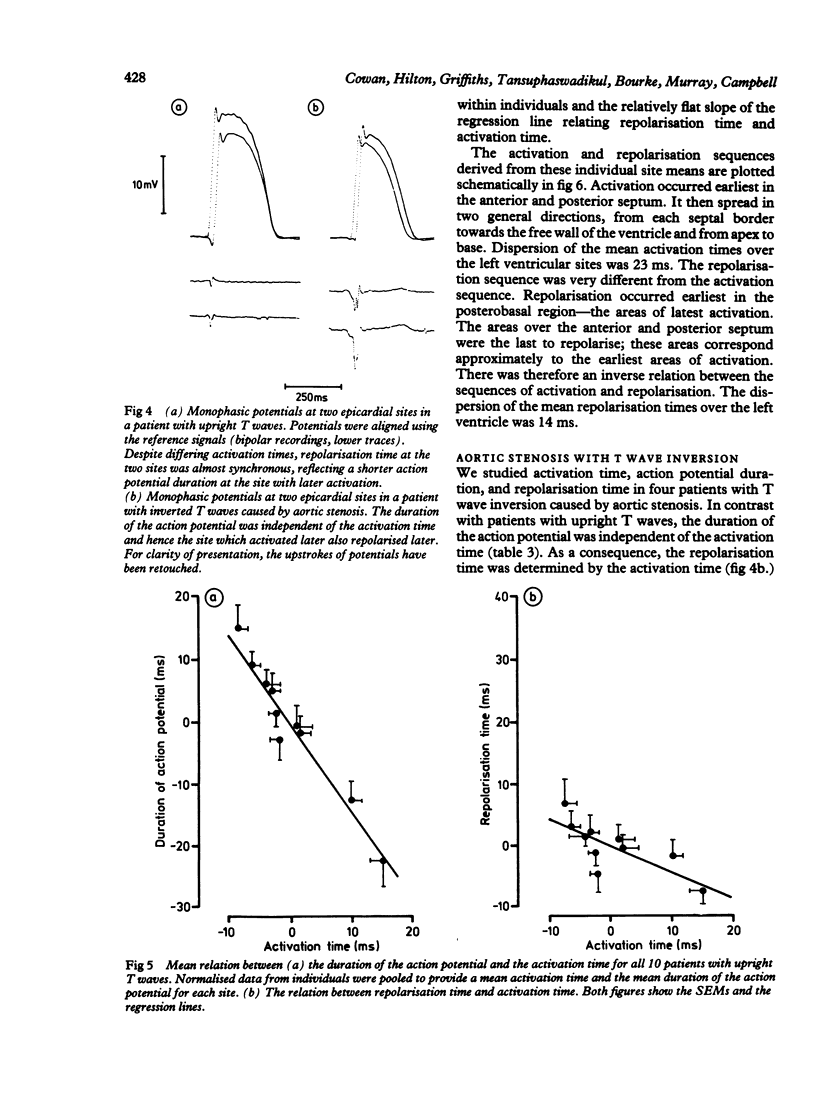
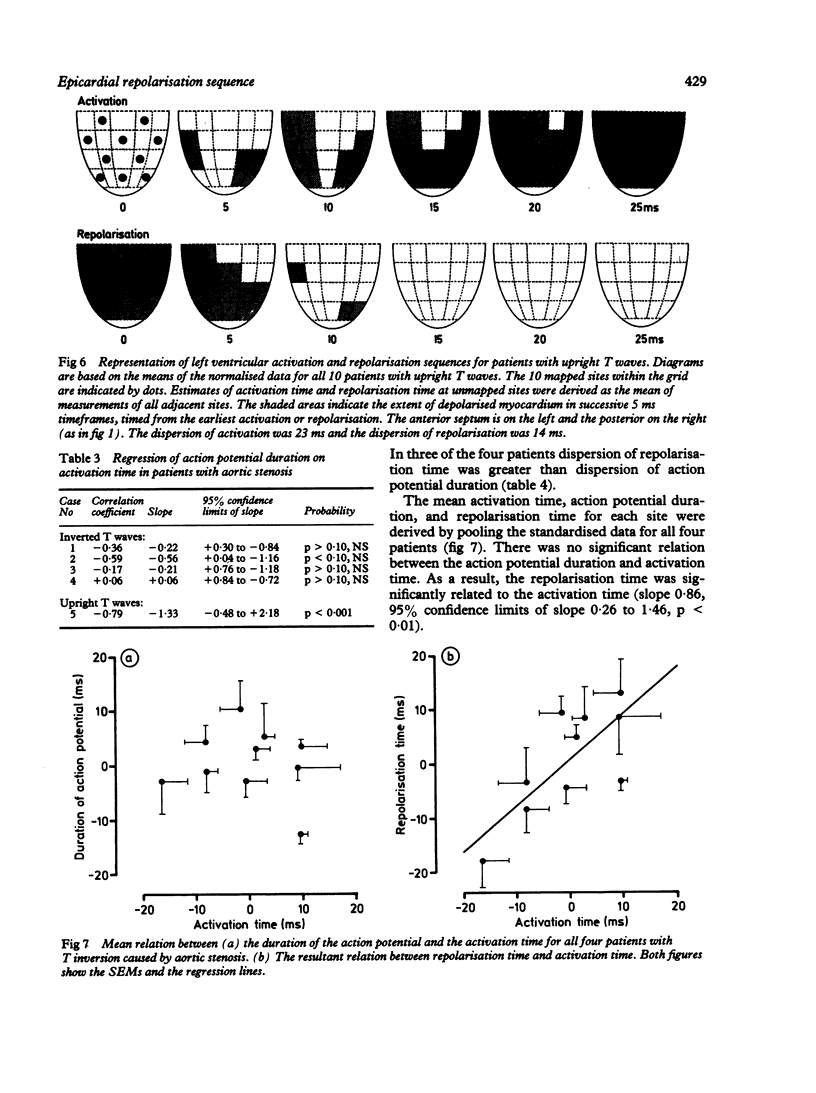
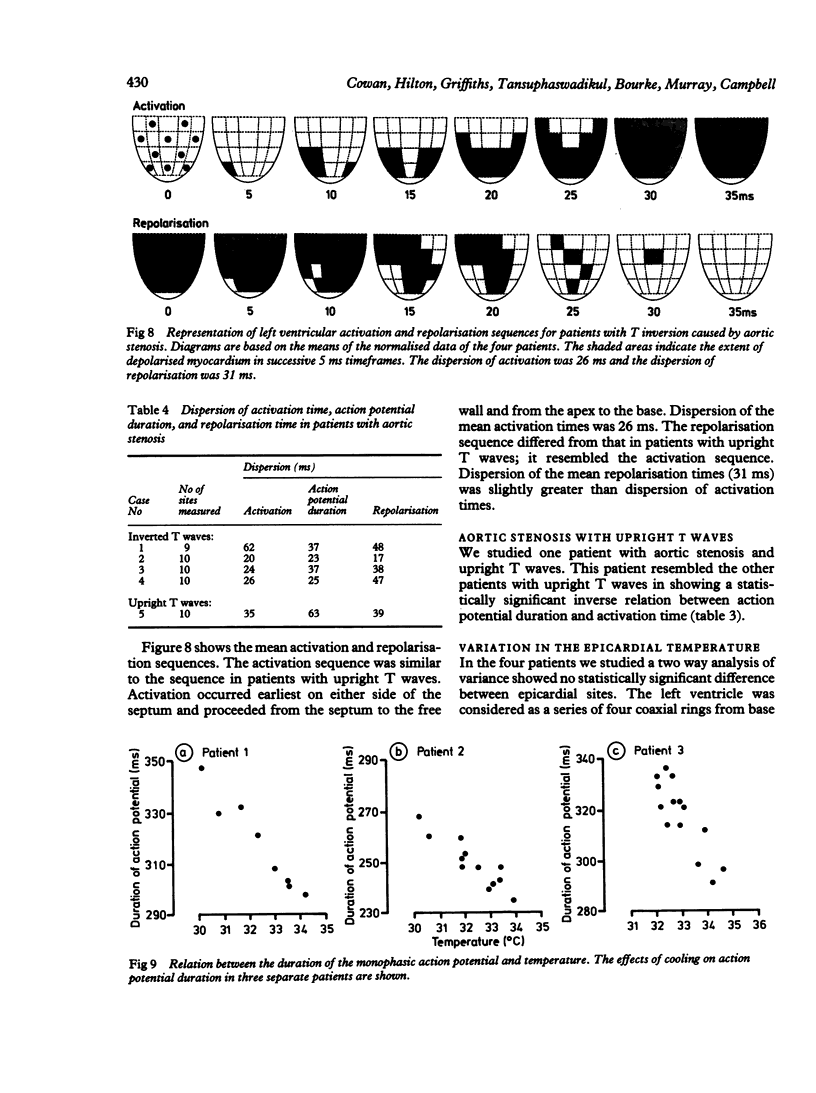
Epicardial activation and repolarisation sequences were investigated in patients with upright or inverted T waves in left ventricular leads of the surface electrocardiogram. Fifteen patients were studied: 10 were undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (upright T waves) and five aortic valve replacement (four patients with T inversion). Monophasic action potentials were recorded intraoperatively from eight to 10 left ventricular sites in each patient. In patients with upright T waves there was an inverse relation between the duration of the monophasic action potential and the activation time (mean slope -1.44). As a consequence, activation and repolarisation proceeded in opposite directions. Dispersion of repolarisation time (14 ms) was less than dispersion of activation time (23 ms). In patients with T wave inversion caused by aortic stenosis there was no relation between the duration of action potential and activation time; the repolarisation sequence resembled the activation sequence, and the dispersion of repolarisation time was greater than the dispersion of activation time (31 and 26 ms respectively). These results show that there are epicardial repolarisation gradients in man and that these are related to the configuration of the T wave. In patients with upright T waves an inverse relation between the duration of the action potential and the activation time reduces the dispersion of the repolarisation time. When the T wave was inverted this relation was no longer found and the dispersion of repolarisation increased.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abildskov J. A. The sequence of normal recovery of excitability in the dog heart. Circulation. 1975 Sep;52(3):442–446. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.52.3.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autenrieth G., Surawicz B., Kuo C. S. Sequence of repolarization on the ventricular surface in the dog. Am Heart J. 1975 Apr;89(4):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(75)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. J., Green L. S., Millar K., Wyatt R., Abildskov J. A. The sequence of normal ventricular recovery. Am Heart J. 1972 Nov;84(5):660–669. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(72)90181-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy D. M., Vassallo J. A., Marchlinski F. E., Buxton A. E., Untereker W. J., Josephson M. E. Endocardial mapping in humans in sinus rhythm with normal left ventricles: activation patterns and characteristics of electrograms. Circulation. 1984 Jul;70(1):37–42. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee K., Harris A., Davies G., Leatham A. Electrocardiographic changes subsequent to artificial ventricular depolarization. Br Heart J. 1969 Nov;31(6):770–779. doi: 10.1136/hrt.31.6.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan J. C., Griffiths C. J., Hilton C. J., Tansuphaswadikul S., Bourke J., Murray A., Campbell R. W. Epicardial repolarization mapping in man. Eur Heart J. 1987 Sep;8(9):952–964. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Bella P., Grazi S., Cipolla C. M., Fabbiocchi F., Rimondini A., Sganzerla P., Guazzi M. D. Increased cardiac electrical instability concomitant with pacing induced repolarisation abnormalities. Br Heart J. 1987 Feb;57(2):118–124. doi: 10.1136/hrt.57.2.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denes P., Pick A., Miller R. H., Pietras R. J., Rosen K. M. A characteristic precordial repolarization abnormality with intermittent left bundle-branch block. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jul;89(1):55–57. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrer D., van Dam R. T., Freud G. E., Janse M. J., Meijler F. L., Arzbaecher R. C. Total excitation of the isolated human heart. Circulation. 1970 Jun;41(6):899–912. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.41.6.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz M. R., Bargheer K., Rafflenbeul W., Haverich A., Lichtlen P. R. Monophasic action potential mapping in human subjects with normal electrocardiograms: direct evidence for the genesis of the T wave. Circulation. 1987 Feb;75(2):379–386. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.2.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz M. R., Burkhoff D., Spurgeon H., Weisfeldt M. L., Lakatta E. G. In vitro validation of a new cardiac catheter technique for recording monophasic action potentials. Eur Heart J. 1986 Jan;7(1):34–41. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a061954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. J., Kasell J. H., Cox J. L., Smith W. M., Ideker R. E., Smith W. M. Techniques of intraoperative electrophysiologic mapping. Am J Cardiol. 1982 Jan;49(1):221–240. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(82)90296-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAN J., GARCIADEJALON P., MOE G. K. ADRENERGIC EFFECTS ON VENTRICULAR VULNERABILITY. Circ Res. 1964 Jun;14:516–524. doi: 10.1161/01.res.14.6.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMAN B. F., CRANEFIELD P. F., LEPESCHKIN E., SURAWICZ B., HERRLICH H. C. Comparison of cardiac monophasic action potentials recorded by intracellular and suction electrodes. Am J Physiol. 1959 Jun;196(6):1297–1301. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.6.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi T., Nakaya Y. T wave polarity related to the repolarization process of epicardial and endocardial ventricular surfaces. Am Heart J. 1984 Aug;108(2):290–295. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. S., Atarashi H., Reddy C. P., Surawicz B. Dispersion of ventricular repolarization and arrhythmia: study of two consecutive ventricular premature complexes. Circulation. 1985 Aug;72(2):370–376. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.2.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. S., Munakata K., Reddy C. P., Surawicz B. Characteristics and possible mechanism of ventricular arrhythmia dependent on the dispersion of action potential durations. Circulation. 1983 Jun;67(6):1356–1367. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.67.6.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirvis D. M. Spatial variation of QT intervals in normal persons and patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Mar;5(3):625–631. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolai P., Medvedowsky J. L., Delaage M., Barnay C., Blache E., Pisapia A. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: T wave abnormalities during normal pathway conduction. J Electrocardiol. 1981 Jul;14(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/s0022-0736(81)80012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum M. B., Blanco H. H., Elizari M. V., Lázzari J. O., Davidenko J. M. Electrotonic modulation of the T wave and cardiac memory. Am J Cardiol. 1982 Aug;50(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(82)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A. D., Klein G. J., Guiraudon G. M., Milstein S. Atrial fibrillation in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: incidence after surgical ablation of the accessory pathway. Circulation. 1985 Jul;72(1):161–169. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spach M. S., Barr R. C. Ventricular intramural and epicardial potential distributions during ventricular activation and repolarization in the intact dog. Circ Res. 1975 Aug;37(2):243–257. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvén J. C., Horacek B. M., Spencer C. A., Klassen G. A., Montague T. J. QT interval variability on the body surface. J Electrocardiol. 1984 Apr;17(2):179–188. doi: 10.1016/s0022-0736(84)81093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart P., Sutton P., Runnalls M., O'Brien W., Donaldson R., Hayward R., Swanton H., Emanuel R., Treasure T. Use of monophasic action potential recordings during routine coronary-artery bypass surgery as an index of localised myocardial ischaemia. Lancet. 1986 Jun 28;1(8496):1462–1465. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91500-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H., Lux R. L., Wyatt R. F., Burgess M., Abildskov J. A. Sequences of early and late phases of repolarization on dog ventricular epicardium. J Electrocardiol. 1981;14(2):143–152. doi: 10.1016/s0022-0736(81)80049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


