Figure 1.
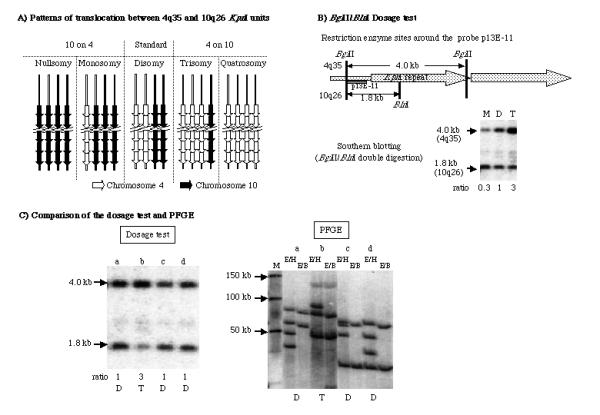
PFGE and the BglII/BlnI dosage test A) Patterns of translocation between chromosome 4q35 and 10q26 KpnI units. Subtelomeric translocation changes the number of BlnI-resistant (from chromosome 4q35) and BlnI-sensitive (from chromosome 10q26) fragments. According to the number of units from chromosome 4, each individual is classified as nullsomy, monosomy, disomy, trisomy or quatrosomy. B) BglII/BlnI dosage test. Double enzyme digestion with BglII and BlnI characterizes the first KpnI unit as a 4.0-kb fragment from chromosome 4q35 or a 1.8-kb fragment from chromosome 10q26. The ratio estimated from the intensity of the two fragments are; nullsomy (N) = 0 (0/4), monosomy (M) = 0.3 (1/3), disomy (D) = 1 (2/2), trisomy (T) = 3 (3/1), and quatrosomy (Q) = infinity (4/0). C) Comparison of the dosage test with PFGE. Thirty Japanese individuals were examined using both PFGE and the dosage test. The ratio from the dosage test was consistent with the results of PFGE in all samples. D: disomy, T: trisomy E/H: EcoRI/HindIII, E/B: EcoRI/BlnI, M: Marker
