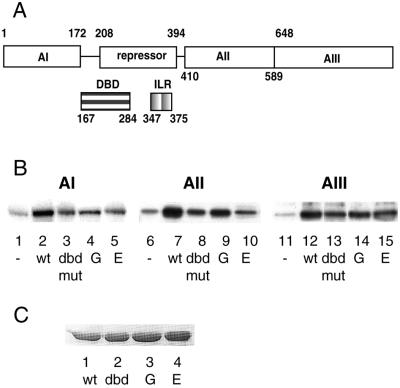
Figure 4.
Binding affinities between DNA-binding domain and activation domains correlate with HSF transcriptional activities. (A) Schematic diagram of domain organization of S. cerevisiae HSF. Amino acid endpoints for each region, as well as their proposed functions, are indicated. (AI, AII, and AIII represent three constitutive activation domains. DBD, DNA-binding domain; IRL, isoleusine repeat (oligomerization domain). This diagram is adapted from the work of Nieto-Sotelo et al. (10). (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of activation domains with wild-type and mutant DBDs. Recombinant wild-type and mutant DBDs were immobilized by anti-GST antibody-coupled protein G Sepharose. Recombinant activation domain I (AI), activation domain II (AII), and activation domain III (AIII) were labeled with [γ-32P]ATP and PKA catalytic subunit. 32P-labeled AI (lanes 1–5), AII (lanes 6–10), and AIII (lanes 11–15) were precipitated by immobilized DBDs. Equal amounts of anti-GST antibody-coupled protein G Sepharose without DBD were used as control to assess nonspecific interactions (lanes 1, 6, and 11). (C) Western blotting analysis of immobilized wild-type and mutant DBDs used in coimmunoprecipitation.