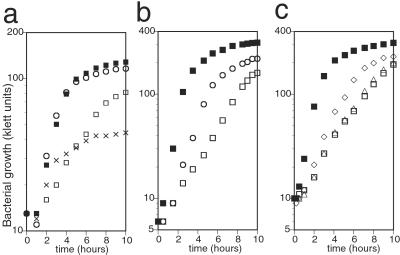
Figure 2.
Effect of hemK knockout and its suppressor mutation on bacterial growth. A fresh overnight culture of each strain was diluted to about 10 klett units (with filter no. 66) in 5 ml of medium and shaken at 37°C. The cell density was determined at intervals, and representative results of the experiments are shown. (a) The growth defect of the hemK knockout strain and complementation by hemK in an expression plasmid. CA293 (hemK+) and CK783 (ΔhemK) were transformed with pAR-hemK or its vector control, pAR3K. The growth of each transformant was examined in casamino acid broth. Essentially the same results were obtained in LB broth. Strains: ■, CA293 pAR3K; □, CK783 pAR3K; ○, CK783 pAR-hemK; x, CK783 pAR-hemK (for x, hemK was induced by adding 50 mg/liter arabinose to the medium at time 0). (b) The growth of the suppressor mutant was compared with that of the hemK+ and ΔhemK strains in LB broth. Strains: ■, LE392 (hemK+); □, LK783 (ΔhemK); ○, LLR201 (one of the suppressor mutants of ΔhemK). (c) The growth of ΔhemK strain transformed with wild-type or mutant prfB in a plasmid was compared with that of the hemK+ or ΔhemK strain in LB broth. Strains: ■, CA293 pMW218 (vector control); □, CK783 pMW218; ▵, CK783 pMW-prfB; ◊, CK783 pMW-prfB(A737G).