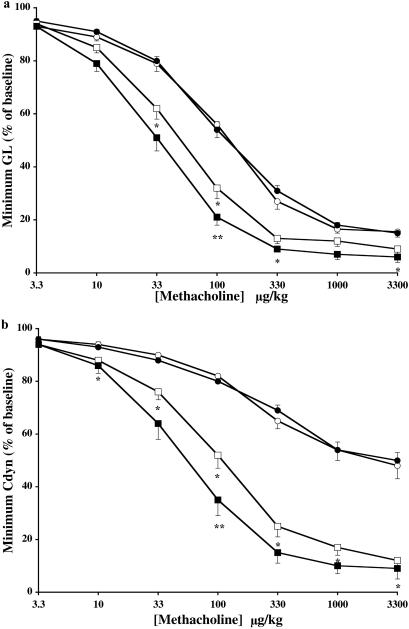
Figure 4.
Assessment of AHR to intravenous MCh in anaesthetized mice. Sham-treated wild-type (○) or CCR3-deficient (●) mice were exposed to aerosolized saline, and OA-sensitized wild-type (□) or CCR3-deficient (■) mice were exposed to aerosolized OA on days 21–24. Approximately 22–26 h after the last aerosol exposure, mice were anaesthetized, intubated, and mechanically ventilated and airway responses to increasing doses of intravenous MCh assessed. The dose–response curves for (a) pulmonary conductance (GL) and (b) pulmonary compliance (Cdyn) are shown. Results are expressed as the means ± SEM (wild-type, n = 10–16; CCR3−/−, n = 10–18 mice/group) of the percent minimal decrease in pulmonary conductance or compliance obtained after MCh challenge compared with the baseline value just before challenge. Significant differences between sham-treated wild-type and sensitized/challenged wild-type mice are indicated as *, P < 0.01–0.002, and significant differences between sensitized/challenged wild-type and sensitized/challenged CCR3−/− mice are indicated as **, P < 0.04, as determined by unpaired Student's t test.