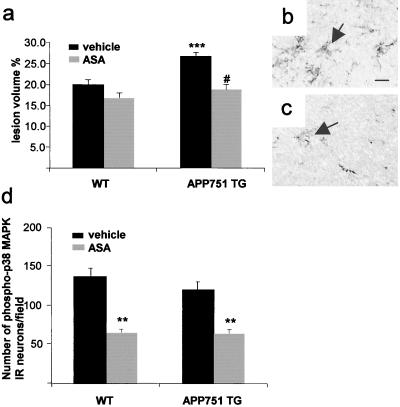
Figure 4.
ASA treatment significantly reduces infarct volume (a, # P < 0.0001 from vehicle-treated APP751 mice, t test) and microgliosis in APP751 TG mice (b and c). (a) ANOVA reveals no difference in lesion volumes between ASA-treated APP751 TG and WT mice but shows larger lesions in vehicle-treated APP751 mice than in any other group (***, P < 0.001, ANOVA, n = 6–8 mice per group). (b) F4/80 positive microglial cells (arrows) in the peri-infarct cortex of a vehicle-treated APP751 TG mouse at 24 h after the MCA occlusion. (c) ASA treatment reduces the number of F4/80 positive microglial cells (arrows) in the perifocal cortex of an APP751 mouse. [Scale bar = 15 μm (b and c)]. (d) Expression of phospho-p38 MAPK in ipsilateral cortical neurons at 30 min after the onset of MCA occlusion is reduced by ASA treatment (**, P < 0.01, when compared with vehicle-treated mice, t test, n = 3 mice per group).