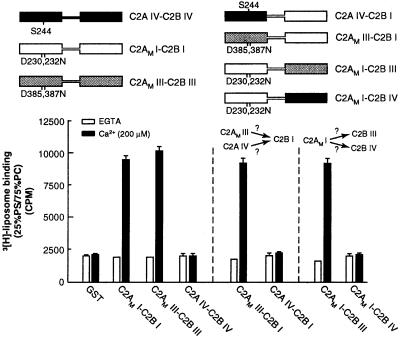
Figure 5.
Syt IV lacks cryptic membrane binding activity within its C2B domain. (Upper) Schematic representations of syt constructs. Regions of isoform I (open rectangles), III (shaded rectangles), or IV (black rectangles) are indicated, as are point mutations that disrupt Ca2+ and membrane-binding activity within the C2A domains of isoforms I and III (designated C2AM; corresponding to D230,232N and D385,387N in syts I and III, respectively). In syt IV, a serine residue is present at position 244; this serine abolishes Ca2+-triggered membrane-binding activity of the isolated C2A domain of the protein and is indicated. (Lower) Six micrograms of glutathione S-transferase-fused versions of the proteins shown (Upper) was immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads. 3H-labeled 25% PS/75% PC liposome-binding assays were carried out as described in Materials and Methods. In these experiments, C2AM I-C2B I and C2AM III-C2B III served as positive controls (13), and, as reported previously, C2A IV-C2B IV failed to bind liposomes (32). C2AM III, but not C2AM IV, activates the liposome-binding activity of C2B I. Furthermore, C2AM I activates the liposome-binding activity of C2B III but not that of C2B IV. These data reveal that the C2A domain of syt IV cannot activate the C2B domain of syt I and that the C2B domain of syt IV cannot be activated by the C2A of syt I.