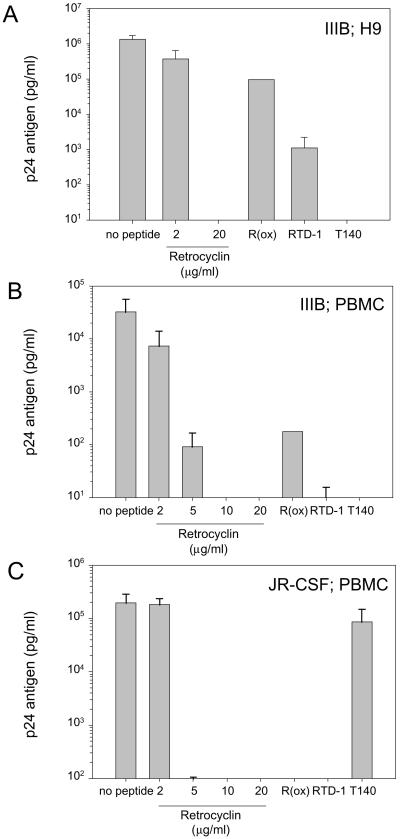
Figure 4.
Anti-HIV-1 activity of retrocyclin. Two strains of HIV-1 and two types of human target cells were used. The IIIB strain is T cell-tropic and utilizes the CXCR4 coreceptor for entry; the JR-CSF strain is M-tropic and uses CCR5 for entry. PBMC signifies CD4+-selected peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Results indicate p24 antigen concentration in pg/ml, as determined by quantitative ELISA assay. (A) Two concentrations of retrocyclin (2 μg/ml, 20 μg/ml), 20 μg/ml of the rhesus circular defensin “RTD-1,” 20 μg/ml of an oxidized and linearized variant of retrocyclin [“R(ox)”], and 20 μg/ml of a horseshoe crab-derived peptide “T140,” which previously was reported to prevent only T cell-tropic infections (25), were tested in antiviral assays of against strain IIIB in H9 cells (n = 2–6 per peptide; error bars indicate SEM). (B) To confirm our results with primary human cells, similar assays were performed by using IIIB virus and CD4+ PBMC or (C) JR-CSF virus and CD4+ PBMC (n = 2–4 per peptide; error bars indicate SEM). Assay sensitivity = 10 pg/ml.