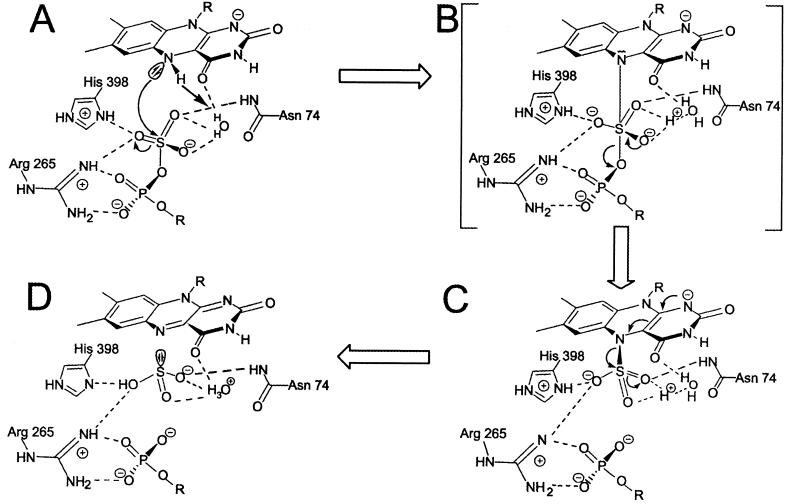
Figure 5.
Scheme of the catalytic mechanism of APS reductase. The mechanism is based on a nucleophilic attack of the atom N5 of FAD on the sulfate sulfur of APS, thus forming a FAD-APS intermediate that decays to AMP and a FAD-sulfite intermediate; the latter was structurally characterized. It is unclear whether the proton of N5 remains in proximity of the active site. It might be transferred to the residues Glu-A141 or Asp-A361.