Table 1.
Site-specific and stepwise binding parameters for the interactions of glycocholic acid with human ileal bile acid binding protein at 20°C
| Parameter type | Dissociation constants*, M | Binding free energies†, kJ/mol |
|---|---|---|
| Site-specific binding | ||
| Cooperativity | 8.6 (± 0.3) × 10−4 | −17.2 ± 0.1 |
| Site 1, intrinsic | 1.5 (± 0.1) × 10−3 | −15.8 ± 0.2 |
| Site 2, intrinsic | 2.1 (± 0.4) × 10−3 | −15.0 ± 0.5 |
| Stepwise binding‡ | ||
| Step 1 | 1.8 (± 0.3) × 10−3 | −15.4 ± 0.4 |
| Step 2 | 1.5 (± 0.9) × 10−6 | −32.6 ± 2.2 |
| Hill coefficient§ | 1.94 |
ΔG° = RTlnKd or RTln(1/c12), where the standard state is defined as 1 M.
The observed stepwise dissociation constants are related to the site-specific dissociation constants as follows: (K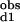 )−1 = (2Kd1)−1 + (2Kd2)−1 and K
)−1 = (2Kd1)−1 + (2Kd2)−1 and K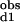 *K
*K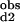 = Kd1*Kd2/c12.
= Kd1*Kd2/c12.
The Hill coefficient, a commonly used measure of macroscopic cooperativity, varies from limiting values of 0 to 2 for extremely negatively and positively cooperative systems, respectively (3). It assumes a value of 1 for a noncooperative system. The Hill coefficient at half saturation is related to the stepwise binding parameters as follows: nH = 2/[1 + (K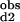 /K
/K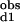 )1/2].
)1/2].
