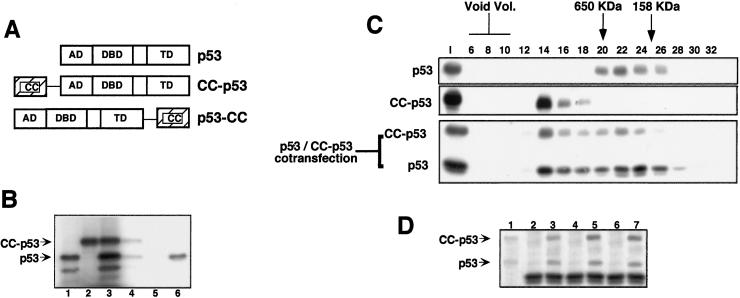
Figure 2.
(A) A schematic view of p53, CC-p53, and p53-CC. AD, activation domain; DBD, DNA binding domain; TD, tetramerization domain. (B) Formation of CC-p53/p53 heterooligomers. P53 (lane 1) and CC-p53 (lane 2) were in vitro-translated singly or cotranslated (lane 3). Samples were then immunoprecipitated with Abs against the CC region of PML (lane 4, from cotranslated CC-p53 and p53; and lane 5, from p53 only) or with an anti-p53-specific Ab (lane 6, from p53 only). (C) CC-p53 recruits wt p53 into high molecular weight complexes. Extracts from p53-null MEFs, transiently transfected with the indicated expression vectors, were subjected to SEC. SEC fractions were then analyzed by Western blot, using the appropriate Ab. The elution volume of mass markers is indicated on the top as previously described. I, input. (D) Extract, or pooled SEC fractions from the p53/CC-p53 cotransfection, was immunoprecipitated with Abs against the CC region of PML and then analyzed by Western blot, using an anti-p53 Ab. Lane 1, input; lanes 2 and 3, immunoprecipitates from input extract; lanes 4 and 5, immunoprecipitates from fractions 13–15; lanes 6 and 7, immunoprecipitates from fractions 20–24; lanes 2, 4, and 6, immunoprecipitates with an unrelated Ab; lanes 3, 5, and 7, immunoprecipitates with the anti-CC Ab.