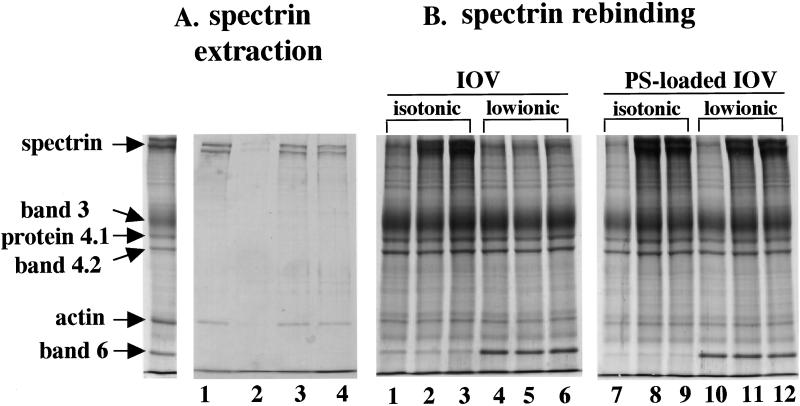
Figure 4.
Interaction of spectrin with membranes in various ghost preparations (A) Protein composition of low ionic buffer (0.5 mM phosphate buffer, pH 8.0) extracts from control ghosts (lane 1), MgATP-ghosts (lane 2), MgATP-ghosts with vanadate (lane 3), and MgAMPPNP-ghosts (lane 4). The far left lane shows the protein composition of native red cell membranes. Note spectrin and actin are extracted from the membranes of control, MgATP ghosts treated with vanadate and MgAMPPNP ghosts but not from MgATP ghosts. (B) Rebinding of purified spectrin dimer to IOVs and PS-loaded IOVs. Spectrin dimer at concentrations of 0.75 mg/ml (lanes 2, 5, 8, and 11) or 1.13 mg/ml (lanes 3, 6, 9, and 12) was added to 0.5 mg of IOVs or PS-loaded IOVs. Spectrin bound to IOVs in isotonic buffer (lanes 2 and 3) but not in low ionic buffer (lanes 5 and 6). However, spectrin bound to PS-loaded IOVs under both isotonic (lanes 8 and 9) and low ionic (lanes 11 and 12) conditions. The protein composition of native IOVs (lanes 1 and 4) and PS-loaded IOVs (lanes 7 and 10) before addition of spectrin are also shown. Note that band 6 remains bound to IOVs under low ionic conditions but is released from IOVs under isotonic conditions.