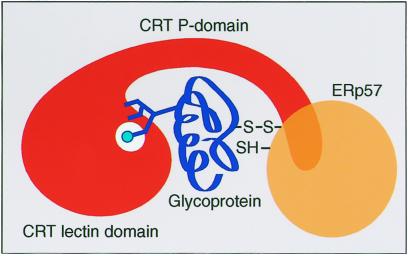
Figure 5.
Scheme for a possible mode of cooperative interaction between CRT and ERp57 in assisting the folding of a glycoprotein based on currently available structural, biochemical, and cell-biological data (2, 7, 8). The substrate glycoprotein (blue) binds to the CRT lectin domain (red) by means of a branched oligosaccharide. CRT and CNX both interact specifically with the Glc1Man9GlaNAc2 form of the oligosaccharide (26–28). The interaction of the terminal glucose (light blue circle) with the binding site (white circle) would place the glycoprotein polypeptide chain in the partially solvent-shielded cavity bounded by the CRT lectin domain, the P-domain, and ERp57 (orange) bound to the distal end of the protruding P-domain. It is further hypothesized that the CRT-ERp57 interaction places the thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase favorably for the formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds (S—S) with the glycoprotein.