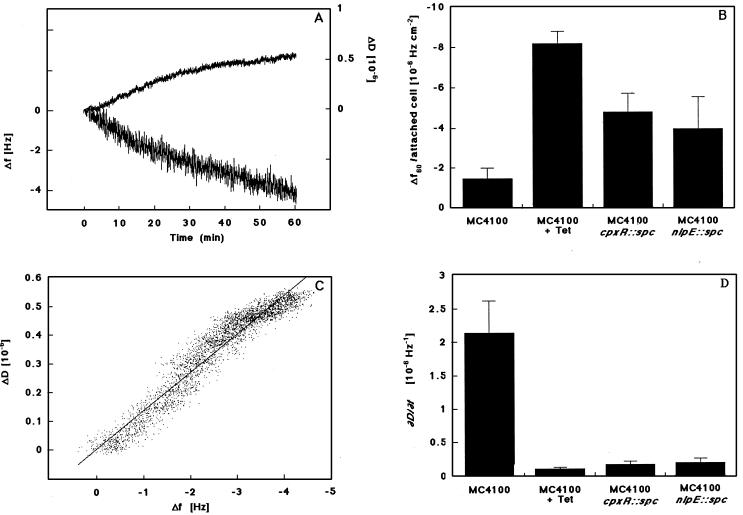
Figure 5.
Cell–surface interactions of E. coli strain MC4100 with hydrophobic surfaces are altered when cpxR or nlpE are absent and resemble the phenotype of wild-type cells in which protein synthesis is inhibited. (A) Representative graph of a real-time measurement of adhesion for strain MC4100 by using the QCM, where relative Δf (lower line) and ΔD (upper line) are shown as a function of time. (B) Δf/attached cell after 60 min of adhesion shown for strains MC4100 in the presence or absence of tetracycline (100 μg⋅ml−1), TR51 (cpxR-null mutant), and WBS262 (nlpE-null mutant). (C) For the same measurement as in A, the ratio of dissipation per Δf (ΔD/Δf) is shown. The slope of this graph (∂D/∂f), derived from a linear curve fit by using kaleidagraph software (Abelbeck Software, Reading, PA), is thought to reflect the viscoelastic properties of the attached cells. (D) The ∂D/∂f is shown for strains MC4100 in the presence or absence of tetracycline (100 μg⋅ml−1), TR51 (cpxR-null mutant), and WBS262 (nlpE-null mutant). Data shown are means (± SD) from 3–5 experiments.