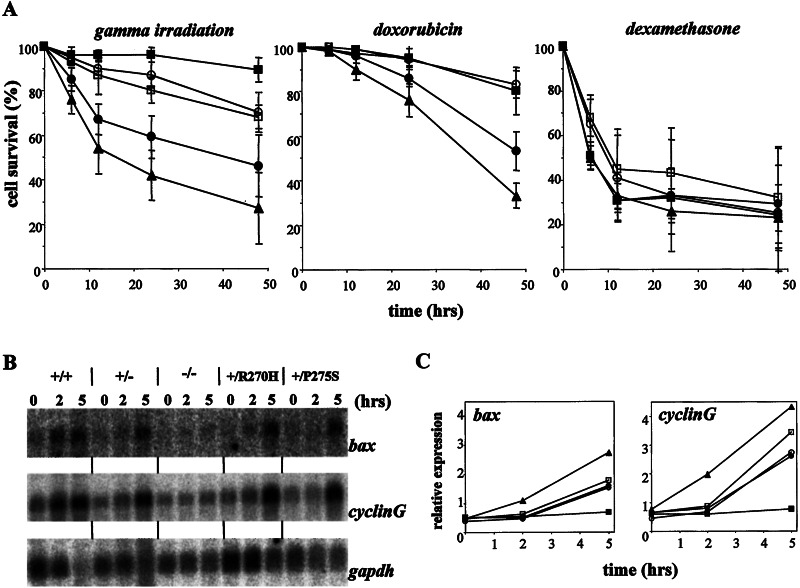
Figure 4.
The effect of heterozygous point mutations in p53 on apoptosis in thymocytes. (A) p53-dependent and -independent apoptosis. Thymocytes of mice of all different genotypes were isolated (▴, wild type; ●, p53+/−; ■, p53−/−; ○, p53+/R270H; □, p53+/P275S) and exposed in vitro to γ irradiation (500 cGy), doxorubicin (0.2 μg/ml), or dexamethasone (1 μM). At the time points indicated, thymocytes were stained with annexin V and PI. The relative percentage of viable cells (negative for both PI and annexin V) for each sample is shown. All values are normalized to the number of cells remaining viable in untreated cultures derived from the same animal stained simultaneously. Data are representatives of ≥2 independent experiments (i.e., mice). (B) Northern blot of p53 target genes in thymocytes after γ irradiation (500 cGy). Two or 5 hr after the treatment, RNA was isolated, and Northern blots were probed with bax, cyclinG, and gapdh cDNA probes. (C) Quantitation of Northern blot signals normalized for expression levels of gapdh (used as a loading control). ▴, Wild type; ●, p53+/−; ■, p53−/−; ○, p53+/R27OH; and □, p53+/P275S.