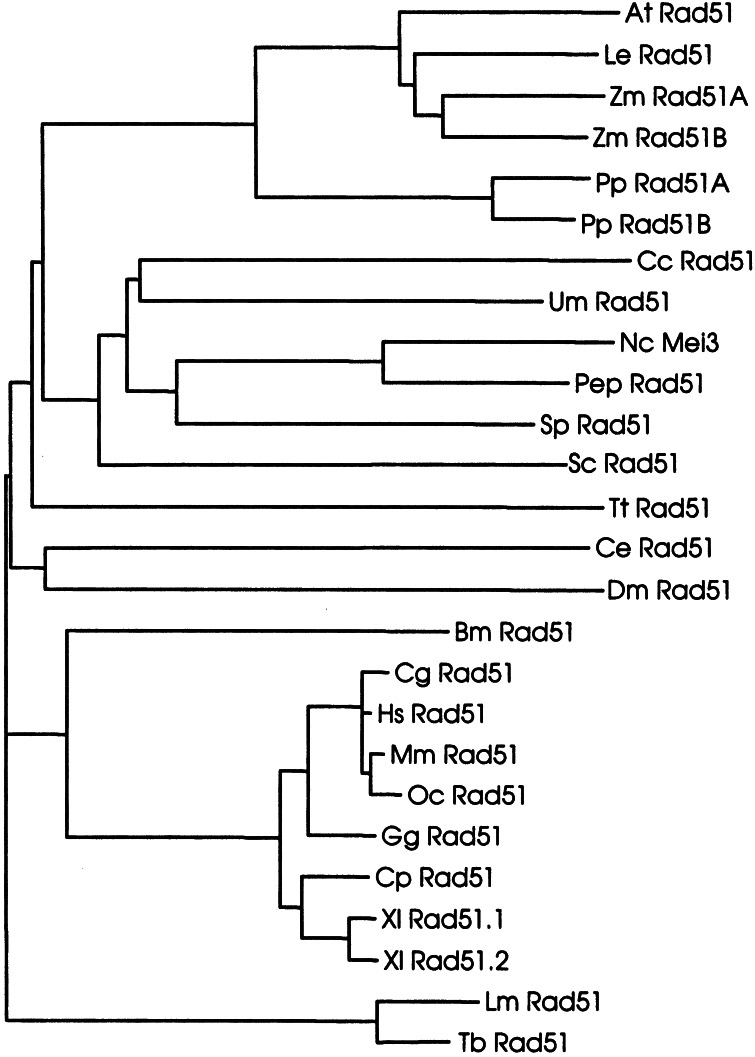
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic relationships of Rad51 proteins. The phylogenetic tree shown is based on amino acid sequence distance and was calculated according to the neighbor-joining algorithm (40). The sequences used for the alignment for the organisms and their accession numbers (in brackets after the abbreviations) are: At, A. thaliana (P94102); Bm, Bombix mori (O01679); Cc, Coprinus cinereus (O074569); Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans (O44246); Cg, Cricetulus griseus (P70099); Cp, Cynops pyrrhogaster (Q9W628); Dm, Drosophila melanogaster (Q27297; Q9VAA8); Gg, Gallus gallus (P37383); Hs, Homo sapiens (Q06609); Le, Lycopersicon esculentum (Q40134); Lm, Leishmania major (O61127); Mm, Mus musculus (Q08297); Nc, N. crassa (P87210); Oc, Oryctolagus cuniculus (O77507); Pep, P. paxilli (Q9P956); PpRad51A, P. patens, this work; Pp Rad51B, P. patens, this work; Sc, S. cerevisiae (P25454); Sp, S. pombe (P36601); Tb, T. brucei (O00847); Tt, T. thermophila (O76341); Um, Ustilago maydis (Q99133); Xl rad51.1, Xenopus laevis (Q91918); Xl Rad51.2, X. laevis (Q91917); Zm Rad51A, Zea mays (Q9XED); Zm Rad51B, Z. mays (Q9XED7).