Figure 4.
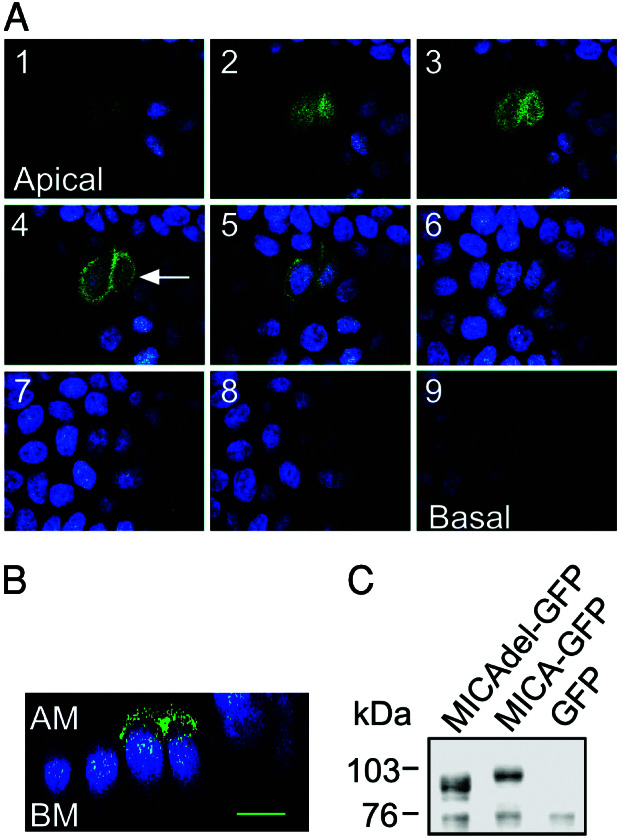
Intracellular localization of GFP-tagged MICA mutant molecules lacking the cytoplasmic domain in polarized MDCK cells. (A) MDCK cells were transiently transfected with the pEGFP-MICAdel plasmid (which lacks the 47 residues C terminus of the protein). Confocal fluorescence micrographs (x–y plane), beginning at the apical membrane (section 1, Upper Left) and ending at the basal membrane (section 9, Lower Right) were acquired in 1.0-μm increments. Arrow in optical section 4 indicates the plane of vertical section. (B) Confocal fluorescence micrograph (x–z plane) shows the distribution of GFP-tagged MICA mutant molecules lacking the cytoplasmic domain along the apical–basal axis. GFP-tagged mutant MICA-derived fluorescence is colored by green and nuclei by blue. AM, apical membrane; BM, basal membrane. The scale bar is 10 μm. (C) Immunoblot analysis of transiently expressed GFP-tagged mutant MICA molecules in MDCK cells. MDCK cells, transiently transfected with the pEGFP-MICA (MICA-GFP) or with pEGFP-MICAdel (MICAdel-GFP) plasmids, were immunoblotted with anti-MICA mouse serum. A control consisted of MDCK cells stably expressing GFP molecules alone. Sizes of marker proteins used in kDa are shown on the left.
