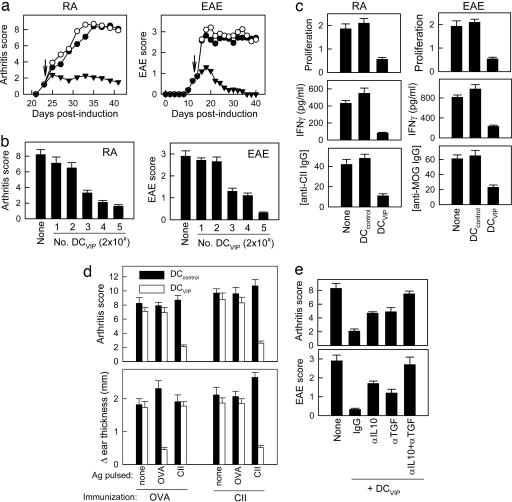
Fig. 3.
Therapeutic effect of DC differentiated with VIP in RA and EAE. (a) DBA1/J mice (H-2q) with established CIA or C57BL/6 mice (H-2b) with established EAE were treated (arrows) with syngeneic CII-pulsed DCs or MOG-pulsed DCs, respectively, generated in the absence (DCcontrol, ○) or presence (DCVIP, ▾ of VIP. Untreated CIA and EAE mice (none, •) were used as controls. Clinical score was monitored (n = 12). (b) CII- and MOG-pulsed DCVIP were injected at different doses. (c) CII-induced proliferation and IFNγ production by spleen T cells, and the levels of anti-CII IgG in sera were determined in CIA mice injected with DCcontrol or DCVIP (n = 5). (d) The effect of DCVIP is Ag-specific. Arthritic mice were treated with unpulsed, CII-pulsed, or OVA-pulsed DCcontrol or DCVIP after disease onset. One week later, mice were immunized s.c. with OVA or CII and challenged i.d. in the ear pinna with the respective Ag 5 d later. Clinical score and DTH responses were determined 24 h later (n = 5). (e) Untreated CIA or EAE mice or animals injected with DCVIP and treated with control Ig, anti-IL10, anti-TGFβ, or a combination of both mAbs (10 mice per group).